Methyltransferase-like 3 facilitates lung cancer progression by accelerating m6A methylation-mediated primary miR-663 processing and impeding SOCS6 expression
- PMID: 35907010
- PMCID: PMC11800879
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04128-5
Methyltransferase-like 3 facilitates lung cancer progression by accelerating m6A methylation-mediated primary miR-663 processing and impeding SOCS6 expression
Abstract
Objective: Lung cancer (LC) remains a threatening health issue worldwide. Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) is imperative in carcinogenesis via m6A modification of microRNAs (miRNAs). This study estimated the effect of METTL3 in LC by regulating m6A methylation-mediated pri-miR-663 processing.
Methods: miR-663 expression in 4 LC cell lines and normal HBE cells was determined using RT-qPCR. A549 and PC9 LC cells selected for in vitro studies were transfected with miR-663 mimics or inhibitor. Cell viability, migration, invasion, proliferation, and apoptosis were detected by CCK-8, Transwell, EdU, and flow cytometry assays. The downstream target genes and binding sites of miR-663 were predicted via Starbase database and validated by dual-luciferase assay. LC cells were delivered with oe-METTL3/sh-METTL3. Crosslinking between METTL3 and DGCR8 was verified by co-immunoprecipitation. Levels of m6A, miR-663, and pri-miR-663 were measured by m6A dot blot assay and RT-qPCR. m6A modification of pri-miR-663 was verified by Me-RIP assay. Finally, the effects of METTL3 in vivo were ascertained by tumor xenograft in nude mice.
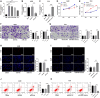
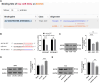
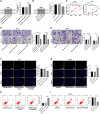
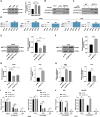
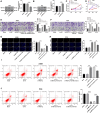
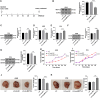
Results: miR-663 was upregulated in LC cells, and miR-663 overexpression promoted cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and inhibited apoptosis, but miR-663 knockdown exerted the opposite effects. miR-663 repressed SOCS6 expression. SOCS6 overexpression annulled the promotion of miR-663 on LC cell growth. METTL3 bound to DGCR8, and METTL3 silencing elevated the levels of pri-miR-663 and m6A methylation-modified pri-miR-663, and suppressed miR-663 maturation and miR-663 expression. METTL3 facilitated tumor growth in mice through the miR-663/SOCS6 axis.
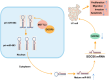
Conclusion: METTL3 promotes LC progression by accelerating m6A methylation-mediated pri-miR-663 processing and repressing SOCS6.
Keywords: Lung cancer; Methyltransferase-like 3; Migration and invasion; Primary miR-663; SOCS6; Tumor formation assay; m6A methylation.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

