Induction of Cross-Reacting Antibodies Against the COVID-19 by BCG Vaccination in the Mouse Model
- PMID: 35907089
- PMCID: PMC9362411
- DOI: 10.1007/s00284-022-02971-w
Induction of Cross-Reacting Antibodies Against the COVID-19 by BCG Vaccination in the Mouse Model
Abstract
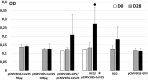
It was reported that tuberculosis and BCG vaccination are potential tools for reducing the burden of COVID-19, mainly through the non-specific trained immunity. We have investigated whether BCG vaccination is able to induce cross-reacting antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2. We have tested the induced humoral immune responses against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike in the mouse model, after either BCG or rabies DNA-based vaccination alone or in Prime/Boost approach to COVID-19 DNA-based vaccination. We have demonstrated that BCG vaccination alone was able to induce cross-reacting antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Spike. It can also boost the antibody response induced by a COVID-19 DNA-based vaccination. Hence, both BCG and latent tuberculosis infection can explain the lower burden of COVID-19 in developing countries, not only through the trained immunity but also by inducing cross-reacting antibodies. Furthermore, with the emergence of different COVID-19 variants, or eventually other Betacoronaviruses, the use of BCG vaccination can help against immune escapes of the current vaccines.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Shivendu S, Chakraborty S, Onuchowska A, Patidar A, Srivastava A. Is there evidence that BCG vaccination has non-specific protective effects for COVID-19 infections or is it an illusion created by lack of testing? SSRN Electronic J. 2020 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3579847. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

