Acute kidney injury associated to COVID-19 leads to a strong unbalance of circulant immune mediators
- PMID: 35907365
- PMCID: PMC9309102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155974
Acute kidney injury associated to COVID-19 leads to a strong unbalance of circulant immune mediators
Abstract
Background: Severe cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have increased risk for acute kidney injury (AKI). The exacerbation of the immune response seems to contribute to AKI development, but the immunopathological process is not completely understood.
Objectives: To analyze levels of circulant immune mediators in COVID-19 patients evolving with or without AKI. We have also investigated possible associations of these mediators with viral load and clinical outcomes.
Methods: This is a longitudinal study performed with hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19. Serum levels of 27 immune mediators were measured by a multiplex immunoassay. Data were analyzed at two timepoints during the follow-up: within the first 13 days of the disease onset (early sample) and from the 14th day to death or hospital discharge (follow-up sample).
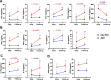
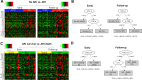
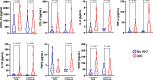
Results: We studied 82 COVID-19 patients (59.5 ± 17.5 years, 54.9% male). Of these, 34 (41.5%) developed AKI. These patients presented higher SARS-CoV-2 viral load (P = 0.03), higher frequency of diabetes (P = 0.01) and death (P = 0.0004). Overall, AKI patients presented significantly higher and sustained levels (P < 0.05) of CCL-2, CCL-3, CCL-4, CXCL-8, CXCL-10, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1Ra, IL-10 and VEGF. Importantly, higher levels of CCL-2, CXCL-10, IL-2, TNF-α, IL-10, FGFb, and VEGF were observed in AKI patients independently of death. ROC curves demonstrated that early alterations in CCL-2, CXCL-8, CXCL-10, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-1Ra and IL-10 show a good predictive value regarding AKI development. Lastly, immune mediators were significantly associated with each other and with SARS-CoV-2 viral load in AKI patients.
Conclusions: COVID-19 associated AKI is accompanied by substantial alterations in circulant levels of immune mediators, which could significantly contribute to the establishment of kidney injury.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; COVID-19; Cytokines; Immune mediators.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Gao Y., Ding M., Dong X., Zhang J., Kursat Azkur A., Azkur D., et al. Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review. Allergy. 2021 Feb;76(2):428–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

