Humoral immune response characterization of heterologous prime-boost vaccination with CoronaVac and BNT162b2
- PMID: 35907676
- PMCID: PMC9352561
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.07.023
Humoral immune response characterization of heterologous prime-boost vaccination with CoronaVac and BNT162b2
Abstract
Background: Vaccination against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has proven to be a successful strategy for prevent severe infections. CoronaVac and BNT162b2 are the most used vaccines worldwide, but their use in heterologous vaccination schedules is still subjected to evaluation.
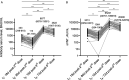
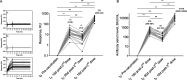
Methods: Fifty healthy individuals who received heterologous prime-boost vaccination with CoronaVac and BNT162b2 were enrolled in a post-vaccination serological follow-up longitudinal prospective study. We evaluated specific serum anti-receptor binding domain (RBD) IgG antibody levels, and their capacity to block RBD-ACE2 interaction with a surrogate neutralization assay. In 20 participants, we assessed antibody binding kinetics by surface plasmon resonance, and Fc-mediated functions by ADCC and ADCP reporter assays.
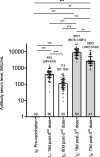
Results: Our baseline seronegative cohort, displayed seroconversion after two doses of CoronaVac and an important decrease in serum anti-RBD IgG antibodies levels 80 days post-second dose. These levels increased significantly early after the third dose with BNT162b2, but 73 days after the booster we found a new fall. Immunoglobulin functionalities showed a similar behavior.
Conclusions: The heterologous prime-boost vaccination with CoronaVac and BNT162b2 generated an impressive increase in serum anti-RBD specific antibody levels followed by a drop. Nevertheless, these titers remained well above those found in individuals only vaccinated with CoronaVac in the same elapsed time. Serum IgG levels showed high correlation with antibody binding analysis, their capacity to block RBD-ACE2 interaction, and Fc-effectors mechanisms. Our work sheds light on the humoral immune response to heterologous vaccination with CoronaVac and BNT162b2, to define a post-vaccination correlate of protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection and to discuss the scheduling of future vaccine boosters in general population.
Keywords: Binding kinetics; Fc-mediated functions; Heterologous vaccination; Humoral immune response; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike receptor binding domain IgG antibody responses after CoronaVac, BNT162b2, ChAdOx1 COVID-19 vaccines, and a single booster dose: a prospective, longitudinal population-based study.Lancet Microbe. 2022 Apr;3(4):e274-e283. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00305-0. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Lancet Microbe. 2022. PMID: 35165669 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 evoked by heterologous vaccination groups using the CoronaVac (Sinovac) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) vaccines in Chile.Front Public Health. 2023 Aug 24;11:1229045. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1229045. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37693706 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing and binding antibody dynamics following primary and booster COVID-19 vaccination among healthcare workers.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 14;25(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10621-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39953414 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of anti-SARS-CoV-2 responses post complete vaccination with coronavac: A prospective study in 50 health workers.J Public Health Res. 2022 Aug 9;11(3):22799036221104173. doi: 10.1177/22799036221104173. eCollection 2022 Jul. J Public Health Res. 2022. PMID: 35966047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding and neutralizing antibody levels and vaccine efficacy/effectiveness compared between heterologous and homologous primary series COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2022 Dec;40(4):321-336. doi: 10.12932/AP-121122-1501. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36681658
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity of Mix-and-Match CoronaVac/BNT162b2 Regimen versus Homologous CoronaVac/CoronaVac Vaccination: A Single-Blinded, Randomized, Parallel Group Superiority Trial.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Aug 5;11(8):1329. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11081329. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631897 Free PMC article.
-
Low switched memory B cells are associated with no humoral response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine boosters in kidney transplant recipients.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 24;14:1202630. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1202630. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37942335 Free PMC article.
-
A Longitudinal Study in Tunisia to Assess the Anti-RBD IgG and IgA Responses Induced by Three Different COVID-19 Vaccine Platforms.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024 Mar 13;9(3):61. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed9030061. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38535885 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Prime-Boost with Immunologically Orthogonal Protein Nanoparticles for Peptide Immunofocusing.ACS Nano. 2024 Jul 23;18(31):20083-100. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c00949. Online ahead of print. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39041587 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble SARS-CoV-2 RBD and human ACE2 peptidase domain produced in Drosophila S2 cells show functions evoking virus-cell interface.Protein Sci. 2023 Aug;32(8):e4721. doi: 10.1002/pro.4721. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37405395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ritchie H, Mathieu E, Rodés-Guirao L, et al. Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19). Our World in Data; 2020. <https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus>.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

