Cancer-testis antigen KK-LC-1 is a potential biomarker associated with immune cell infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35907786
- PMCID: PMC9339200
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09930-5
Cancer-testis antigen KK-LC-1 is a potential biomarker associated with immune cell infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Cancer-testis antigens (CTAs) have emerged as potential clinical biomarkers targeting immunotherapy. KK-LC-1 is a member of CTAs, which has been demonstrated in a variety of tumors tissues and been found to elicit immune responses in cancer patients. However, the expression level and immune infiltration role of KK-LC-1 in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) remains to be elucidated.
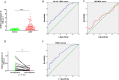
Methods: In this study, the mRNA expression and overall survival rate of KK-LC-1 were evaluated by the TIMER and TCGA database in LUAD tissues and KK-LC-1 expression was further validated by clinical serum samples using quantitative RT-PCR. The relationship of KK-LC-1 with clinicopathologic parameters was analyzed. ROC curve result showed that miR-1825 was able to distinguish preoperative breast cancer patients from healthy people and postoperative patients. Then, the ROC curves were used to examine the ability of KK-LC-1 to distinguish preoperative LUAD patients from healthy and postoperative patients. The correlation between KK-LC-1 and infiltrating immune cells and immune marker sets was investigated via TIMER, TISIDB database, and CIBERSORT algorithm. The Kaplan-Meier plotter was used to further evaluate the prognostic value based on the expression levels of KK-LC-1 in related immune cells.
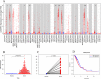
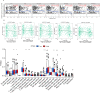
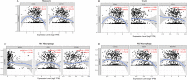
Results: The results showed that KK-LC-1 was significantly over-expressed in LUAD, and high levels of expression of KK-LC-1 were also closely correlated with poor overall survival. We also found that KK-LC-1 associated with TMN stage, NSE and CEA. The ROC curve result showed that KK-LC-1 was able to distinguish preoperative LUAD cancer patients from healthy people and postoperative patients. Moreover, KK-LC-1 had a larger AUC with higher diagnostic sensitivity and specificity than CEA. Based on the TIMER, TISIDB database, and CIBERSORT algorithm, the expression of KK-LC-1 was negatively correlated with CD4+ T cell, Macrophage, and Dendritic Cell in LUAD. Moreover, Based on the TIMER database, KK-LC-1 expression had a remarkable correlation with the type markers of Monocyte, TAM, M1 Macrophage, and M2 Macrophage. Furthermore, KK-LC-1 expression influenced the prognosis of LUAD patients by directly affecting immune cell infiltration by the Kaplan-Meier plotter analysis.
Conclusions: In conclusion, KK-LC-1 may serve as a promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in LUAD and correlate with immune infiltration and prognosis.
Keywords: Cancer-testis antigen; KK-LC-1; Lung adenocarcinoma; Prognosis; Tumor immune infiltration.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer testis antigen MAGEA3 in serum and serum-derived exosomes serves as a promising biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 30;14(1):7573. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58003-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38555374 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer/testis antigen HEMGN correlated with immune infiltration serves as a prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma.Mol Immunol. 2023 Jan;153:226-237. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.12.008. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36563642
-
Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3G (PPP1R3G) correlates with poor prognosis and immune infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):8336-8346. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1985817. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34592886 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic potential value of Cancer-testis antigens in immunotherapy of gastric cancer.Gene. 2023 Feb 15;853:147082. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.147082. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Gene. 2023. PMID: 36464170 Review.
-
Cancer testis antigens as immunogenic and oncogenic targets in breast cancer.Immunotherapy. 2018 Jul;10(9):769-778. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0179. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Immunotherapy. 2018. PMID: 29926750 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Validation of a Cancer-Testis Antigen-Related Signature to Predict the Prognosis in Stomach Adenocarcinoma.J Cancer. 2024 May 11;15(11):3596-3611. doi: 10.7150/jca.91842. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38817874 Free PMC article.
-
CT83 Promotes Cancer Progression by Upregulation of PDL1 in Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 17;26(6):2687. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062687. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141328 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Stem Cells Connecting to Immunotherapy: Key Insights, Challenges, and Potential Treatment Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;17(13):2100. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132100. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KK-LC-1, a biomarker for prognosis of immunotherapy for primary liver cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 7;24(1):811. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12586-y. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38972967 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Exploration of Small Molecule Binders for CT83: Computational Insights from Homology Modeling, Virtual Screening, MD Simulations, Interaction Fingerprint, and Network Communications.ACS Omega. 2025 May 23;10(22):22884-22908. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00053. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40521510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I, Kowalski DM, Cho BC, Turna HZ, Castro G, Jr, Srimuninnimit V, Laktionov KK, Bondarenko I, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10183):1819–1830. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32409-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

