What is the impact of a novel DEPDC5 variant on an infant with focal epilepsy: a case report
- PMID: 35907814
- PMCID: PMC9338555
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-022-03515-8
What is the impact of a novel DEPDC5 variant on an infant with focal epilepsy: a case report
Abstract
Background: Variants in the DEPDC5 have been proved to be main cause of not only various dominant familial focal epilepsies, but also sporadic focal epilepsies. In the present study, a novel variant in DEPDC5 was detected in the patient with focal epilepsy and his healthy father. We aimed to analyze the pathogenic DEPDC5 variant in the small family of three.
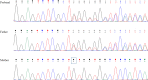
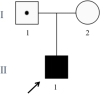
Case presentation: A 5-month-old male infant presented with focal epilepsy. Whole exome sequencing identified a novel heterozygous variant c.1696delC (p.Gln566fs) in DEPDC5, confirmed by Sanger sequencing. The variant was inherited from healthy father.
Conclusions: Our study expands the spectrum of DEPDC5 variants. Moreover, We discuss the relation between the low penetrance of DEPDC5 and the relatively high morbidity rate of DEPDC5-related sporadic focal epilepsy. Besides, due to interfamilial phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity, we speculate the prevalence of familial focal epilepsy with variable foci might be underestimated in such small families. We emphasize the importance of gene detection in patients with sporadic epilepsy of unknown etiology, as well as their family members. It can identify causative mutations, thus providing help to clinicians in making a definitive diagnosis.
Keywords: Case report; DEPDC5; FFEVF; Focal epilepsy; Whole exome sequencing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DEPDC5 mutations in familial and sporadic focal epilepsy.Clin Genet. 2017 Oct;92(4):397-404. doi: 10.1111/cge.12992. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Clin Genet. 2017. PMID: 28170089
-
Mutations in DEPDC5 cause familial focal epilepsy with variable foci.Nat Genet. 2013 May;45(5):546-51. doi: 10.1038/ng.2599. Epub 2013 Mar 31. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23542697
-
Magnetoencephalogram-assisted diagnosis of familial focal epilepsy with variable foci in a Chinese family with a novel DEPDC5 mutation.Epileptic Disord. 2019 Jun 1;21(3):289-294. doi: 10.1684/epd.2019.1066. Epileptic Disord. 2019. PMID: 31225799 Review.
-
A recurrent mutation in DEPDC5 predisposes to focal epilepsies in the French-Canadian population.Clin Genet. 2014 Dec;86(6):570-4. doi: 10.1111/cge.12311. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Clin Genet. 2014. PMID: 24283814
-
DEPDC5 plays a vital role in epilepsy: Genotypic and phenotypic features in cohort and literature.Epileptic Disord. 2024 Jun;26(3):341-349. doi: 10.1002/epd2.20223. Epub 2024 May 16. Epileptic Disord. 2024. PMID: 38752894 Review.
References
-
- Bar-Peled L, Chantranupong L, Cherniack AD, Chen WW, Ottina KA, Grabiner BC, Spear ED, Carter SL, Meyerson M, Sabatini DM. A Tumor suppressor complex with GAP activity for the Rag GTPases that signal amino acid sufficiency to mTORC1. Science. 2013;340(6136):1100–1106. doi: 10.1126/science.1232044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

