Distribution and clinical significance of circulating CD8+CD28- regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 35907816
- PMCID: PMC9338636
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-022-02088-7
Distribution and clinical significance of circulating CD8+CD28- regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: Regulatory T cells (Treg cells) in the peripheral blood of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) may be closely related to the progression of PTB. In this study, the distribution characteristics and clinical importance of CD8+CD28- Treg cells in patients with tuberculosis were systematically analyzed, and the role and importance of CD8+CD28- Treg cells in influencing the immune response and progression of tuberculosis were discussed, which will provide immunological indices and reference values for the clinical diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Methods: Flow cytometry, sputum smears and computed tomography imaging were used to analyze the distribution characteristics of CD8+CD28- Treg cells in the peripheral blood of patients with PTB and the correlation between CD8+CD28-Treg cells and clinical and immune indices.
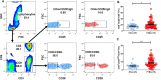
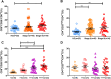
Results: The percentages of CD4+CD25high and CD8+CD28- Treg cells in the peripheral blood of patients with PTB were significantly higher than those in the healthy control (HC) group. Further analysis showed that the percentage of CD4+CD25highTreg cells in the Stage II group was significantly higher than that in the HC group. The percentages of CD4+CD25high and CD8+CD28- Treg cells increased significantly in patients in the Stage II group. The proportion of CD8+CD28- Treg cells was directly proportional to the degree of positivity in sputum smears, while CD4+CD25highTreg cells did not exhibit this trend. The correlations between the percentage of CD4+CD25high and CD8+CD28- Treg cells and the percentage of lymphocyte subsets were examined. The percentage of CD8+CD28- Treg cells was negatively correlated with the percentage of CD4+T cells and positively correlated with the CD8+T cell percentage in the HC and PTB groups. The percentage of CD4 + CD25highTreg cells was positively correlated with the percentage of CD4+T cells only in the PTB group.
Conclusions: This study was the first to show that the proportion of CD8+CD28- Treg cells in the peripheral blood of patients with PTB was significantly increased, and the increase in CD8+CD28- Treg cells was related to the progression of PTB, which may affect the proportion of immune cell subsets by inhibiting the immune response, resulting in the progression of PTB.
Keywords: CD8+CD28− Treg; Immune response; Tuberculosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD8+CD28- cells and CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of advanced stage lung cancer patients.Med Oncol. 2010 Mar;27(1):29-33. doi: 10.1007/s12032-008-9165-9. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Med Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19148592
-
[Correlation study between changes in intestinal microflora structure and immune indexes in newly treated patients with pulmonary tuberculosis].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Dec 6;55(12):1486-1490. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20210728-00721. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34963248 Chinese.
-
[The expression of T cell costimulatory molecules and the proportion of NK cells in peripheral blood of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Jul;40(7):629-635. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39179406 Chinese.
-
Changes of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ and CD8+CD28- regulatory T cells in non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing surgery.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Feb;18(2):255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24345703
-
Harnessing CD8+CD28- Regulatory T Cells as a Tool to Treat Autoimmune Disease.Cells. 2021 Nov 1;10(11):2973. doi: 10.3390/cells10112973. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study.Open Life Sci. 2023 Feb 9;18(1):20220557. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0557. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36816803 Free PMC article.
-
A Key Role of CD8+ T Cells in Controlling of Tuberculosis Infection.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;13(18):2961. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13182961. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761328 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct characteristics of BTLA/HVEM axis expression on Tregs and its impact on the expansion and attributes of Tregs in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 25;14:1437207. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1437207. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39386167 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical significance of plasma sCD25 as valuable biomarker for progression and prognosis of tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 22;24(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08798-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38254003 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SKY2021061, SS2019074, GSWS2019067, SZYJTD201716 and LCZX202116/the Science and Technology Plan of Suzhou, China, grant number
- SKY2021061, SS2019074, GSWS2019067, SZYJTD201716 and LCZX202116/the Science and Technology Plan of Suzhou, China, grant number
- SKY2021061, SS2019074, GSWS2019067, SZYJTD201716 and LCZX202116/the Science and Technology Plan of Suzhou, China, grant number
- SKY2021061, SS2019074, GSWS2019067, SZYJTD201716 and LCZX202116/the Science and Technology Plan of Suzhou, China, grant number
- SKY2021061, SS2019074, GSWS2019067, SZYJTD201716 and LCZX202116/the Science and Technology Plan of Suzhou, China, grant number
- SKY2021061, SS2019074, GSWS2019067, SZYJTD201716 and LCZX202116/the Science and Technology Plan of Suzhou, China, grant number
- SKY2021061, SS2019074, GSWS2019067, SZYJTD201716 and LCZX202116/the Science and Technology Plan of Suzhou, China, grant number
- KJXW2020048/Youth Science and Technology Project of Suzhou city
- 81900577/National Natural Science Foundation
- 81900577/National Natural Science Foundation
- 81900577/National Natural Science Foundation
- BZ2019017/the Science and Technology Plan of Jiangsu, China,
- BZ2019017/the Science and Technology Plan of Jiangsu, China,
- BZ2019017/the Science and Technology Plan of Jiangsu, China,
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

