Blockade of the amino acid transporter SLC6A14 suppresses tumor growth in colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 35907820
- PMCID: PMC9339205
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09935-0
Blockade of the amino acid transporter SLC6A14 suppresses tumor growth in colorectal Cancer
Abstract
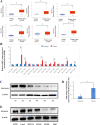
Background: The amino acid transporter SLC6A14, which transports 18 of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, is too low to be detected in healthy normal tissues but is significantly increased in some solid cancers. However, little is known about the roles of SLC6A14 in colorectal cancer (CRC).
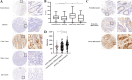
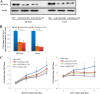
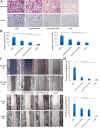
Methods: The mRNA and protein levels of SLC6A14 were detected using TCGA database, real-time polymerase chain reaction, western blot, and tissue microarrays, respectively. Amino acids concentration was determined by LC-MS/MS. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were determined using MTT assay and flow cytometry. Transwell invasion assay and wound healing assay were employed to analyze cell migration and invasion. The protein levels of Akt-mTOR signaling pathway and MMPs proteins were detected by western blot.
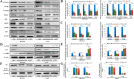
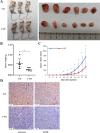
Results: Both of the mRNA and protein levels of SLC6A14 were upregulated in CRC tissues, and the protein levels of SLC6A14 were closely related to the tumor cells differentiation: the higher the expression of SLC6A14 was, the poorer the differentiation of the tumor cells was. Further knockdown SLC6A14 with siRNA or treatment with α-MT in CRC cell lines reduced cell proliferation and migration in vitro and inhibited xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistically, SLC6A14 was demonstrated to regulate the expression and phosphorylation of Akt-mTOR, which mediates the promoting tumor growth function of SLC6A14. Blockade of SLC6A14 with α-MT inhibited the activation of mTOR signaling.
Conclusion: SLC6A14 was upregulated in CRC and could promote tumor progression by activating the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway, which may serve as an effective molecular target for the treatment of CRC.
Keywords: Amino acid transporter; Colorectal cancer; SLC6A14; mTOR; α-Methyltryptophan.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SLC6A14, a Na+/Cl--coupled amino acid transporter, functions as a tumor promoter in colon and is a target for Wnt signaling.Biochem J. 2020 Apr 30;477(8):1409-1425. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200099. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32219372 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate Reductase-2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression via Activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway.Dis Markers. 2021 Sep 1;2021:9950663. doi: 10.1155/2021/9950663. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34512817 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the amino acid transporter Slc6a14 suppresses tumour growth in spontaneous mouse models of breast cancer.Biochem J. 2015 Jul 1;469(1):17-23. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150437. Epub 2015 May 13. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26173258
-
The up-regulated lncRNA DLX6-AS1 in colorectal cancer promotes cell proliferation, invasion and migration via modulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Oct;23(19):8321-8331. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201910_19143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31646562
-
MicroRNA-7 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via TYRO3 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein B kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway suppression.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Nov;42(5):2503-2514. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3864. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30226533 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CALD1 inhibits invasion of human ovarian cancer cells by affecting cytoskeletal structure and the number of focal adhesion.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):1323-1335. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1375. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40104711 Free PMC article.
-
Altered carnitine transporter genes (SLC22A5, SLC22A16, SLC6A14) expression pattern among lung cancer patients.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):2903-2917. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-448. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39670016 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Apr;55(4):706-715. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00971-9. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37009798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-methyltryptophan-mediated protection against diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice as studied with a metabolomics approach.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 20;15:1463673. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1463673. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39902076 Free PMC article.
-
LAT1-specific PET radiotracers: Development and clinical experiences of a new class of cancer-specific radiopharmaceuticals.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 2;15(5):1864-1878. doi: 10.7150/thno.99490. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39897549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barberini L, Restivo A, Noto A, Deidda S, Fattuoni C, Fanos V, et al. A gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) metabolomic approach in human colorectal cancer (CRC): the emerging role of monosaccharides and amino acids. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(23):727. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.34. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

