Hospitals during economic crisis: a systematic review based on resilience system capacities framework
- PMID: 35907833
- PMCID: PMC9339182
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-022-08316-4
Hospitals during economic crisis: a systematic review based on resilience system capacities framework
Abstract
Background: Hospitals are the biggest users of the health system budgets. Policymakers are interested in improving hospital efficiency while maintaining their performance during the economic crisis. This study aims at analysing the hospitals' policy solutions during the economic crisis using the resilience system capacities framework.
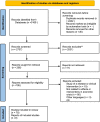
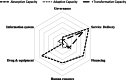
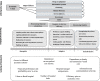
Method: This study is a systematic review. The search strategy was implemented on the Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, Scopus databases, and Econbiz search portal. Data were extracted and analysed through the comparative table of resilience system capacities framework and the World Health Organization (WHO) health system's six building blocks (i.e., leadership and governance, service delivery, health workforce, health systems financing, health information systems, and medicines and equipment).
Findings: After the screening, 78 studies across 36 countries were reviewed. The economic crisis and adopted policies had a destructive effect on hospital contribution in achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC). The short-term absorptive capacity policies were the most frequent policies against the economic crisis. Moreover, the least frequent and most effective policies were adaptive policies. Transformative policies mainly focused on moving from hospital-based to integrated and community-based services. The strength of primary care and community-based services, types and combination of hospital financing systems, hospital performance before the crisis, hospital managers' competencies, and regional, specialties, and ownership differences between hospitals can affect the nature and success of adopted policies.
Conclusion: The focus of countries on short-term policies and undermining necessary contextual factors, prioritizing efficiency over quality, and ignoring the interrelation of policies compromised hospital contribution in UHC.
Keywords: Economic crisis; Hospital; Resilience.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis for health system resilience against the economic crisis: a best-fit framework synthesis.Health Res Policy Syst. 2025 Mar 14;23(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12961-025-01285-0. Health Res Policy Syst. 2025. PMID: 40087656 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative analysis of Iranian sixth five-year economic, social, and cultural development plan from universal health coverage perspective.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Sep 14;21(1):966. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06985-1. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34521388 Free PMC article.
-
The influential factors for achieving universal health coverage in Iran: a multimethod study.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Jul 22;21(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06673-0. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34294100 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Health Care Systems and Their Contribution to Universal Health Coverage and Improved Health Status in Seven Countries: An Explanatory Mixed-Methods Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Nov 30;21(12):1601. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21121601. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39767442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successes and challenges of health systems governance towards universal health coverage and global health security: a narrative review and synthesis of the literature.Health Res Policy Syst. 2022 May 2;20(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12961-022-00858-7. Health Res Policy Syst. 2022. PMID: 35501898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Autonomy Reform on the Efficiency of Public Hospitals in China: A DEA-ITSA Combination Analysis.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025 Apr 16;18:1333-1346. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S514512. eCollection 2025. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025. PMID: 40255881 Free PMC article.
-
The Road Ahead and Challenges of Revenue Cycle Management in Saudi Governmental Hospitals.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;11(20):2716. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11202716. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37893790 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare organizations in crisis context: decision-making models and roles of CEOs.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Feb 18;25(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12420-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 39966924 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Economic Aspects of Hospitals: A Comprehensive Examination of Relevant Factors.Cureus. 2024 Feb 25;16(2):e54867. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54867. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38533171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A resilience view on health system resilience: a scoping review of empirical studies and reviews.BMC Health Serv Res. 2023 Nov 24;23(1):1297. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10022-8. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023. PMID: 38001460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Monetary Fund. World Economic Outlook, April 2009: crisis and recovery: International Monetary Fund; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical