Ultra-thin layered double hydroxide-mediated photothermal therapy combine with asynchronous blockade of PD-L1 and NR2F6 inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35907841
- PMCID: PMC9338598
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01565-9
Ultra-thin layered double hydroxide-mediated photothermal therapy combine with asynchronous blockade of PD-L1 and NR2F6 inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is limited due to low levels of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes and deficient checkpoint blockade in this immunologically "cool" tumor. Thus, combination approaches are needed to increase the response rates of ICB and induce synergistic antitumor immunity.
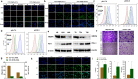
Methods: Herein, we designed a pH-sensitive multifunctional nanoplatform based on layered double hydroxides (LDHs) loaded with siRNA to block the intracellular immune checkpoint NR2F6, together with the asynchronous blockade surface receptor PD-L1 to induce strong synergistic antitumor immunity. Moreover, photothermal therapy (PTT) generated by LDHs after laser irradiation modified an immunologically "cold" microenvironment to potentiate Nr2f6-siRNA and anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy. Flow cytometry was performed to assess the immune responses initiated by the multifunctional nanoplatform.
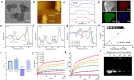
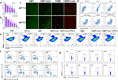
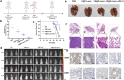
Results: Under the slightly acidic tumor extracellular environment, PEG detached and the re-exposed positively charged LDHs enhanced tumor accumulation and cell uptake. The accumulated siRNA suppressed the signal of dual protumor activity in both immune and H22 tumor cells by silencing the NR2F6 gene, which further reduced the tumor burden and enhanced systemic antitumor immunity. The responses include enhanced tumor infiltration by CD4+ helper T cells, CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, and mature dendritic cells; the significantly decreased level of immune suppressed regulator T cells. The therapeutic responses were also attributed to the production of IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α. The prepared nanoparticles also exhibited potential magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ability, which could serve to guide synergistic immunotherapy treatment.
Conclusions: In summary, the three combinations of PTT, NR2F6 gene ablation and anti-PD-L1 can promote a synergistic immune response to inhibit the progression of primary HCC tumors and prevent metastasis. This study can be considered a proof-of-concept for the targeting of surface and intracellular immune checkpoints to supplement the existing HCC immunotherapy treatments.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NR2F6; PD-L1 blockade; Photothermal therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Xu J, Zheng Q, Cheng X, Hu S, Zhang C, Zhou X, Sun P, Wang W, Su Z, Zou T, Song Z, Xia Y, Yi X, Gao Y. Chemo-photodynamic therapy with light-triggered disassembly of theranostic nanoplatform in combination with checkpoint blockade for immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):355–355. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01101-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

