Design of predictive model to optimize the solubility of Oxaprozin as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- PMID: 35907929
- PMCID: PMC9338975
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17350-5
Design of predictive model to optimize the solubility of Oxaprozin as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Abstract
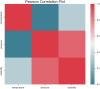
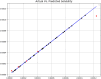
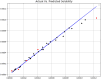
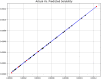
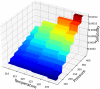
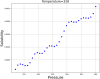
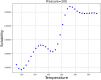
These days, many efforts have been made to increase and develop the solubility and bioavailability of novel therapeutic medicines. One of the most believable approaches is the operation of supercritical carbon dioxide fluid (SC-CO2). This operation has been used as a unique method in pharmacology due to the brilliant positive points such as colorless nature, cost-effectives, and environmentally friendly. This research project is aimed to mathematically calculate the solubility of Oxaprozin in SC-CO2 through artificial intelligence. Oxaprozin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug which is useful in arthritis disease to improve swelling and pain. Oxaprozin is a type of BCS class II (Biopharmaceutical Classification) drug with low solubility and bioavailability. Here in order to optimize and improve the solubility of Oxaprozin, three ensemble decision tree-based models including random forest (RF), Extremely random trees (ET), and gradient boosting (GB) are considered. 32 data vectors are used for this modeling, moreover, temperature and pressure as inputs, and drug solubility as output. Using the MSE metric, ET, RF, and GB illustrated error rates of 6.29E-09, 9.71E-09, and 3.78E-11. Then, using the R-squared metric, they demonstrated results including 0.999, 0.984, and 0.999, respectively. GB is selected as the best fitted model with the optimal values including 33.15 (K) for the temperature, 380.4 (bar) for the pressure and 0.001242 (mole fraction) as optimized value for the solubility.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhuang W, Hachem K, Bokov D, Ansari MJ, Nakhjiri AT. Ionic liquids in pharmaceutical industry: A systematic review on applications and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liquids. 2021;349:118145. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118145. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

