Fabrication of polyamide-12/cement nanocomposite and its testing for different dyes removal from aqueous solution: characterization, adsorption, and regeneration studies
- PMID: 35907938
- PMCID: PMC9338974
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16977-8
Fabrication of polyamide-12/cement nanocomposite and its testing for different dyes removal from aqueous solution: characterization, adsorption, and regeneration studies
Abstract
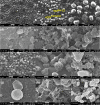
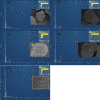
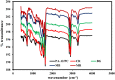
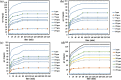
Polyamide-12/Portland cement nanocomposite was prepared by using the exfoliated adsorption method. The fabricated nanocomposite was applied first time to remove Congo red (CR), brilliant green (BG), methylene blue (MB), and methyl red (MR) from the synthetic wastewater. The polymer nanocomposite was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, elemental mapping, Brunauer-Emmett-Teller surface area analysis, and X-ray diffraction. The adsorption was rapid and all the studied dyes were absorbed on the surface of the polymer nanocomposite in 90 min. The point of zero charge was found at pH 5 and the factors such as pH, time, and temperature were found to affect the adsorption efficiency. Freundlich isotherm and pseudo-second-order models well-fitted the adsorption isotherm and kinetics data, respectively. The calculated maximum adsorption capacity was 161.63, 148.54, 200.40, and 146.41 mg/g for CR, BG, MB, and MR, respectively. The mode of the adsorption process was endothermic, spontaneous, and physical involving electrostatic attraction. On an industrial scale, the high percentage of desorption and slow decrease in the percentage of adsorption after every five regeneration cycles confirm the potential, practicality, and durability of the nanocomposite as a promising and advanced adsorbent for decolorization of colored wastewater.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Baig U, Uddin MK, Gondal MA. Removal of hazardous azo dye from water using synthetic nano adsorbent: Facile synthesis, characterization, adsorption, regeneration and design of experiments. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020;584:124031. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124031. - DOI
-
- Uddin MK, Mashkoor F, Al-Arifi I, Nasar A. Simple one-step synthesis process of novel MoS2@bentonite magnetic nanocomposite for efficient adsorption of crystal violet from aqueous solution. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111279. - DOI
-
- Uddin MK, Bushra R. Synthesis and characterization of composite cation-exchange material and its application in removing toxic pollutants. Enhancing Cleanup of Environ. Pollut. 2017 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55423-5_9. - DOI
-
- Khan MA, Uddin MK, Bushra R, Ahmad A, Nabi SA. Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline Zr(IV) molybdophosphate for the adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2014;113:499–517. doi: 10.1007/s11144-014-0751-x. - DOI
-
- Uddin MK, Baig U. Synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles and their performance towards methyl orange dye removal: Characterisation, adsorption and response surface methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 2019;211:1141–1153. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.232. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

