Conjunctival sac bacterial culture of patients using levofloxacin eye drops before cataract surgery: a real-world, retrospective study
- PMID: 35907940
- PMCID: PMC9338605
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-022-02544-2
Conjunctival sac bacterial culture of patients using levofloxacin eye drops before cataract surgery: a real-world, retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The use of antibiotics preoperatively is effective to decrease the incidence of ocular bacterial infections but may lead to high resistance rate, especially on patients with multi-risk clinical factors. This study systematically analyzed real-world data (RWD) of patients to reveal the association between clinical factors and conjunctival sac bacterial load and offer prophylaxis suggestions.
Methods: We retrieved RWD of patients using levofloxacin eye drops (5 mL: 24.4 mg, 4 times a day for 3 days) preoperatively. Retrieved data included information on the conjunctival sac bacterial culture, sex, presence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus (DM), and history of hospital-based surgeries. Data was analyzed using SPSS 24.0.
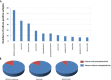
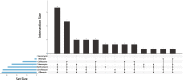
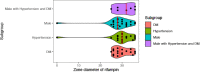
Results: RWD of 15,415 cases (patients) were retrieved. Among these patients, 5,866 (38.1%) were males and 9,549 (61.9%) females. 5,960 (38.7%) patients had a history of hypertension, and 3,493 (22.7%) patients had a history of DM. 7,555 (49.0%) patients had a history of hospital-based operations. There were 274 (1.8%) positive bacterial cultures. Male patients with hypertension and DM may be at increased risk of having positive bacterial cultures (P < 0.05). Staphylococcus epidermidis (n = 56, 20.4%), Kocuria rosea (n = 37, 13.5%), and Micrococcus luteus (n = 32, 11.7%) were the top 3 isolated strains. Most bacterial strains were resistant to various antibiotics except rifampin, and 82.5% (33 of 40 isolates) of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates had multidrug antibiotic resistance. Numbers of culture-positive Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates in the male group and non-DM group were greater than those in the female and DM groups, respectively. Micrococcus luteus (n = 11, 8.8%) was found less frequently in non-hypertension group than in hypertension group.
Conclusion: Sex (Male) and the presence of hypertension and DM are risk factors for greater conjunctival sac bacterial loads. We offer a prophylactic suggestion based on the combined use of levofloxacin and rifampin. However, this approach may aggravate risk of multidrug resistance.
Keywords: Antibiotic prophylactic therapy; Clinical factor; Levofloxacin; Real world study.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of iodine compounds and levofloxacin as postoperative instillation; conjunctival bacterial flora and antimicrobial susceptibility following cataract surgery.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2024 Nov;68(6):702-708. doi: 10.1007/s10384-024-01117-8. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39240403
-
Effect of the administration period of perioperative topical levofloxacin on normal conjunctival bacterial flora.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017 Jan;43(1):42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2016.10.024. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017. PMID: 28317676 Clinical Trial.
-
[Susceptibility of drug-resistant staphylococci isolated from different parts of the ocular anterior segment to common ophthalmic antibiotics].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Aug 11;58(8):598-605. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112142-20220119-00023. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35959604 Chinese.
-
[Clinical study on the reduction of ocular surface bacteria in pre-operative cataract surgery patients by cleansing the eyelid margins].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 11;54(6):445-451. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2018.06.011. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29895119 Chinese.
-
Optimal Duration for the Use of 0.5% LevofloxacinEye Drops Before Vitreoretinal Surgery.Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2017 Jan-Feb;6(1):40-44. doi: 10.22608/APO.2015197. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2017. PMID: 28161927 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effects of autologous serum and artificial tears on corneal sensation and tear film stability in patients with mild to moderate xerophthalmia after cataract surgery.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan 24;45(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03402-4. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39853569 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluating and Managing the Microbial Contamination of Eye Drops: A Two-Phase Hospital-Based Study.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 12;16(7):933. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070933. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065630 Free PMC article.
-
Conjunctival microbiota variations in a subset of middle-aged and elderly individuals from Beijing, China.Int J Ophthalmol. 2025 Feb 18;18(2):237-243. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2025.02.06. eCollection 2025. Int J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39967978 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput sequencing reveals differences in microbial community structure and diversity in the conjunctival tissue of healthy and type 2 diabetic mice.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Mar 16;24(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03247-y. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38493114 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

