Pharmacotherapy consideration of thrombolytic medications in COVID-19-associated ARDS
- PMID: 35908022
- PMCID: PMC9338522
- DOI: 10.1186/s40560-022-00625-4
Pharmacotherapy consideration of thrombolytic medications in COVID-19-associated ARDS
Abstract
Background: In late 2019, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) which is responsible for coronavirus disease (COVID-19), was identified as the new pathogen to lead pneumonia in Wuhan, China, which has spread all over the world and developed into a pandemic. Despite the over 1 year of pandemic, due to the lack of an effective treatment plan, the morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 remains high. Efforts are underway to find the optimal management for this viral disease.
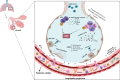
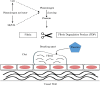
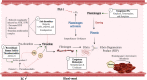
Main body: SARS-CoV-2 could simultaneously affect multiple organs with variable degrees of severity, from mild to critical disease. Overproduction of pro-inflammatory mediators, exacerbated cellular and humoral immune responses, and coagulopathy such as Pulmonary Intravascular Coagulopathy (PIC) contributes to cell injuries. Considering the pathophysiology of the disease and multiple microthrombi developments in COVID-19, thrombolytic medications seem to play a role in the management of the disease. Beyond the anticoagulation, the exact role of thrombolytic medications in the management of patients with COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is not explicit. This review focuses on current progress in underlying mechanisms of COVID-19-associated pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy, the historical use of thrombolytic drugs in the management of ARDS, and pharmacotherapy considerations of thrombolytic therapy, their possible benefits, and pitfalls in COVID-19-associated ARDS.
Conclusions: Inhaled or intravenous administration of thrombolytics appears to be a salvage therapy for severe ARDS associated with COVID-19 by prompt attenuation of lung injury. Considering the pathogenesis of COVID-19-related ARDS and mechanism of action of thrombolytic agents, thrombolytics appear attractive options in stable patients without contraindications.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; Coagulopathy; Pharmacotherapy; Pro-inflammatory; Thrombolytic therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare to have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Turk C, Turk S, Malkan U, Haznedaroglu IC. Three critical clinicobiological phases of the human SARS-associated coronavirus infections. 2020. - PubMed
-
- Sahebnasagh A, Mojtahedzadeh M, Najmeddin F, Najafi A, Safdari M, Ghaleno HR, et al. A perspective on erythropoietin as a potential adjuvant therapy for acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with COVID-19. Arch Med Res. 2020;51:631. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.08.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous