Effect of dexamethasone on intraoperative remifentanil dose in total knee arthroplasty surgery under general anaesthesia
- PMID: 35908167
- PMCID: PMC9543467
- DOI: 10.1111/aas.14118
Effect of dexamethasone on intraoperative remifentanil dose in total knee arthroplasty surgery under general anaesthesia
Abstract
Background: The effects of glucocorticoids may include both genomic and rapid nongenomic effects. The potential rapid analgesic effect during surgery has not previously been investigated. We aimed to explore the effect of dexamethasone on intraoperative infusion rate of remifentanil in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty (TKA) surgery under general anaesthesia.
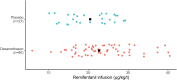
Methods: In this post hoc subgroup analysis, we included patients randomised in the DEX-2-TKA trial, who were operated under total intravenous anaesthesia with remifentanil and propofol. Trial medication, intravenous dexamethasone 24 mg or placebo, was administered immediately after anaesthesia onset. The primary outcome was the median weight-corrected infusion rate of remifentanil during surgery. Secondary outcomes included median weight-corrected infusion rate of propofol, median intraoperative bispectral index and time spent in the post-anaesthesia care unit.
Results: Eighty-seven patients were included in the analysis of the primary outcome. A significantly higher remifentanil infusion rate was observed in the dexamethasone group compared with the placebo group, p = .02. None of the secondary outcomes resulted in statistically significant differences between groups.
Conclusion: This explorative post hoc analysis of the randomised DEX-2-TKA trail showed that patients undergoing TKA surgery under general anaesthesia and who received dexamethasone seemed to have a higher remifentanil infusion rate compared with patients who received placebo. The clinical implications of the potentially increased remifentanil infusion rate need to be validated and explored further.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05002361 (12 August 2021).
Keywords: alloplastic surgery; dexamethasone; glucocorticoid; intraoperative pain; intraoperative remifentanil; remifentanil anaesthesia; total knee arthroplasty; total knee replacement.
© 2022 The Authors. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ole Mathiesen is an associate editor at Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. Christian Sylvest Meyhoff is an associate editor at Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. Christian Sylvest Meyhoff has co‐founded a start‐up company, WARD247 ApS, with the aim of pursuing the regulatory and commercial activities of the WARD‐project (Wireless Assessment of Respiratory and circulatory Distress, a project developing a clinical support system for continuous wireless monitoring of vital signs). WARD247 ApS has obtained licence agreement for any WARD‐project software and patents. One patent has been filed: “Wireless Assessment of Respiratory and circulatory Distress (WARD)—Clinical Support System (CSS)—an automated clinical support system to improve patient safety and outcomes”. Christian Sylvest Meyhoff reports in addition direct and indirect departmental research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Merck, Sharp & Dohme as well as lecture fees from Radiometer. Otherwise, no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lunn TH, Kristensen BB, Andersen L, et al. Effect of high‐dose preoperative methylprednisolone on pain and recovery after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 2011;106:230‐238. - PubMed
-
- Holte K, Kehlet H. Perioperative single‐dose glucocorticoid administration: pathophysiologic effects and clinical implications.J. Am Coll Surg. 2002;195:694‐712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical