Ritodrine in external cephalic version: is it effective and safe?
- PMID: 35908652
- PMCID: PMC9483666
- DOI: 10.5468/ogs.22106
Ritodrine in external cephalic version: is it effective and safe?
Abstract
Objective: The external cephalic version (ECV) has been shown to lower the likelihood of cesarean section requirements among pregnant women with breech presentations. In the current study, we investigated the effectiveness and safety of ritodrine as a tocolytic for ECV.
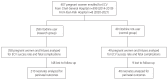
Methods: A total of 407 pregnant women with breech presentations, who had no contraindications for ECV, were enrolled in this study. Multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to assess the impact of ritodrine use on the safety and efficacy of ECV.
Results: The overall success rate was 67.6%, and ritodrine use was associated with significantly higher odds of successful ECV after adjusting for confounders. Moreover, using ritodrine did not increase the risk of adverse effects, including temporary changes in fetal heart rate, need for elective or emergency cesarean section due to fetal distress during ECV, low Apgar scores, and perinatal mortality.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that using ritodrine as a tocolytic during ECV may increase the likelihood of ECV success and may not increase adverse perinatal outcomes.
Keywords: External cephalic version; Pregnancy; Pregnancy outcomes; Ritodrine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO statement on caesarean section rates. Geneva: WHO; 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources