The importance of monitoring wet age-related macular degeneration patients during Coronavirus disease 19 pandemic: A retrospective study of assessment of functional and structural outcomes
- PMID: 35908993
- PMCID: PMC9257228
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfo.2022.05.005
The importance of monitoring wet age-related macular degeneration patients during Coronavirus disease 19 pandemic: A retrospective study of assessment of functional and structural outcomes
Abstract
Objectives: Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injections are the gold standard treatment for wet age-related macular degeneration (wet AMD). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has led to the cancellation of many scheduled intravitreal anti-VEGF injection visits. We compared the functional and structural visual outcomes of wet AMD patients who did not adhere to their planned intervals (group 1) with those who did (group 2).
Methods: Wet AMD patients of Swiss Visio Montchoisi and RétinElysée were included. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) changes between their first visit after the end of the first national lockdown in Switzerland (27 April 2020, first post-lockdown visit) and their last visit before the beginning of the first national lockdown in Switzerland (13 March 2020, last pre-lockdown visit) were assessed. The BCVA outcome was defined as unfavorable when there was a loss of≥5 ETDRS letters in the first post-lockdown visit compared to the BCVA at last pre-lockdown visit. The OCT outcome was defined as unfavorable when there was an increase in at least one of the parameters, intraretinal fluid (IRF), subretinal fluid (SRF), or pigment epithelial detachment (PED), at the first post-lockdown visit compared to the last pre-lockdown visit.
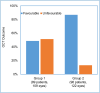
Main results: Group 1 (89 patients, 109 eyes) had a 13.41% greater rate of unfavorable BCVA outcomes and a 38.27% greater rate of unfavorable OCT outcomes than group 2 (96 patients, 122 eyes) (P=0.04, P<0.0001, respectively). Multivariate analysis showed that the more the patients deviated from their programmed injections and the higher the BCVA pre-lockdown, the higher the rate of unfavorable BCVA outcomes (P=0.03 and P=0.02, respectively). OCT outcomes were not a predictive factor for an unfavorable BCVA outcome.
Conclusions: The cancellation of many intravitreal anti-VEGF injection appointments resulted in worse functional and structural outcomes in wet AMD patients. The COVID-19 pandemic led many patients to refrain from their routine intravitreal anti-VEGF injection appointments, allowing us to analyze the role of designated intervals in the treatment of wet AMD. During any future lockdown due to COVID-19 or similar circumstances, continuity of care for wet AMD patients should be maintained.
Objectifs: Les injections intravitréennes d’anti-facteur de croissance vasculaire endothélial (anti-VEGF) constituent le traitement de référence de la dégénérescence maculaire liée à l’âge (DMLA). La maladie à coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) a entraîné l’annulation de nombreuses visites programmées. Nous avons comparé les résultats visuels et structurels des patients atteints de DMLA qui n’ont pas respecté les intervalles prévus (groupe 1) à ceux qui les ont respectés (groupe 2).
Méthodes: Les patients atteints de DMLA de notre clinique ont été inclus. La meilleure acuité visuelle corrigée (BCVA) et les changements par tomographie en cohérence optique (OCT) entre leur première visite après la fin du premier confinement national en Suisse (27 avril 2020, première visite post-confinement) et leur dernière visite avant le début du premier confinement national en Suisse (13 mars 2020, dernière visite pré-confinement) ont été évalués. Le résultat de la BCVA était défavorable en cas de perte de ≥ 5 lettres ETDRS lors de la première visite post-confinement par rapport à la valeur de BCVA de la dernière visite pré-confinement. Le résultat de l’OCT était défavorable lorsqu’il y avait une augmentation d’au moins un des éléments suivants : liquide intrarétinien (IRF), liquide sous-rétinien (SRF) ou décollement de l’épithélium pigmentaire (PED) lors de la première visite post-confinement par rapport à la dernière visite pré-confinement.
Résultats principaux: Le groupe 1 (89 patients, 109 yeux) présentait un taux d’évolution défavorable de la BCVA de 13,41 % et un taux d’évolution défavorable de l’OCT de 38,27 % supérieurs à ceux du groupe 2 (96 patients, 122 yeux) (p = 0,04, p < 0,0001, respectivement). L’analyse multivariée a montré que plus les patients s’écartaient des injections programmées et plus la BCVA était élevée avant le confinement, plus le taux de résultats de BCVA défavorables était élevé (p = 0,03 et p = 0,02, respectivement). Le résultat de l’OCT n’était pas un facteur prédictif d’un résultat défavorable de la BCVA.
Conclusion: L’annulation de nombreux rendez-vous d’injections intravitréennes d’anti-VEGF a entraîné une détérioration des résultats fonctionnels et structurels chez les patients atteints de DMLA humide. Lors d’un prochain confinement dû au COVID-19, la continuité des soins pour les patients atteints de DMLA devra être maintenue.
Keywords: Anti-VEGF; Anti-facteur de croissance endothélial vasculaire; Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor; COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 2019; DMLA; Dégénérescence maculaire liée à l’âge humide; Maladie à coronavirus 2019; Wet AMD; Wet age-related macular degeneration.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The association of exudation pattern with anatomical and functional outcomes in patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2019 Jul-Sep;63(3):238-244. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31687625 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment patterns and visual acuity change of AMD patients, before, during and after the COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns: A large cohort.Acta Ophthalmol. 2024 May;102(3):e322-e327. doi: 10.1111/aos.15756. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37698269
-
The effect of COVID-19 pandemic restrictions on neovascular AMD patients treated with treat-and-extend protocol.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep;41(9):2951-2961. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01854-6. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33864577 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Visual Acuity and Residual Retinal Fluid Following Intravitreal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun 1;140(6):611-622. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.1357. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35551359 Free PMC article.
-
Defining response to anti-VEGF therapies in neovascular AMD.Eye (Lond). 2015 Jun;29(6):721-31. doi: 10.1038/eye.2015.48. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Eye (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25882328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing visual outcomes of nAMD treatment during and after the COVID-19 restrictions period.PLoS One. 2025 May 7;20(5):e0323253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323253. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40333806 Free PMC article.
-
Patient Perspective on the Monitoring of Their Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration during Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Mar 2;59(3):490. doi: 10.3390/medicina59030490. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36984491 Free PMC article.
-
Patient adherence to therapy after switch to aflibercept from bevacizumab or ranibizumab for treatment-refractory neovascular age-related macular degeneration.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jan 1;72(Suppl 1):S101-S105. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_1795_23. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38131550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pascolini D., Mariotti S.P., Pokharel G.P., Pararajasegaram R., Etya’ale D., Négrel A.D., et al. 2002 global update of available data on visual impairment: a compilation of population-based prevalence studies. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2004;11:67–115. - PubMed
-
- Friedman D.S., O’Colmain B.J., Muñoz B., Tomany S.C., McCarty C., de Jong P.T.V.M., et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:564–572. - PubMed
-
- Li J.Q., Welchowski T., Schmid M., Mauschitz M.M., Holz F.G., Finger R.P. Prevalence and incidence of age-related macular degeneration in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2020;104:1077–1084. - PubMed
-
- Salmon J.F. In: KANSKI'S clinical ophthalmology: a systematic approach. 9th ed. Salmon J.F., editor. Elsevier; United Kingdom: 2020. Age-related macular degeneration; p. 572.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

