Where would Canadians prefer to die? Variation by situational severity, support for family obligations, and age in a national study
- PMID: 35909120
- PMCID: PMC9340714
- DOI: 10.1186/s12904-022-01023-1
Where would Canadians prefer to die? Variation by situational severity, support for family obligations, and age in a national study
Abstract
Background: Death at home has been identified as a key quality indicator for Canadian health care systems and is often assumed to reflect the wishes of the entire Canadian public. Although research in other countries has begun to question this assumption, there is a dearth of rigorous evidence of a national scope in Canada. This study addresses this gap and extends it by exploring three factors that moderate preferences for setting of death: situational severity (entailing both symptoms and supports), perceptions of family obligation, and respondent age.
Methods: Two thousand five hundred adult respondents from the general population were recruited using online panels between August 2019 and January 2020. The online survey included three vignettes, representing distinct dying scenarios which increased in severity based on symptom management alongside availability of formal and informal support. Following each vignette respondents rated their preference for each setting of death (home, acute/intensive care, palliative care unit, nursing home) for that scenario. They also provided sociodemographic information and completed a measure of beliefs about family obligations for end-of-life care.
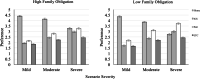
Results: Home was the clearly preferred setting only for respondents in the mild severity scenario. As the dying scenario worsened, preferences fell for home death and increased for the other options, such that in the severe scenario, most respondents preferred a palliative care or hospice setting. This pattern was particularly distinct among respondents who also were less supportive of family obligation norms, and for adults 65 years of age and older.
Conclusions: Home is not universally the preferred setting for dying. The public, especially older persons and those expressing lower expectations of families in general, express greater preference for palliative care settings in situations where they might have less family or formal supports accompanied by more severe and uncontrolled symptoms. Findings suggest a) the need for public policy and health system quality indicators to reflect the nuances of public preferences, b) the need for adequate investment in hospices and palliative care settings, and c) continuing efforts to ensure that home-based formal services are available to help people manage symptoms and meet their preferences for setting of death.
Keywords: Canada; Dying preferences; Family care; Palliative care; Perception; Place of death; Public policy; Surveys and questionnaires.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Social and clinical determinants of preferences and their achievement at the end of life: prospective cohort study of older adults receiving palliative care in three countries.BMC Geriatr. 2017 Nov 23;17(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12877-017-0648-4. BMC Geriatr. 2017. PMID: 29169346 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, Attitudes, and Preferences of Advance Decisions, End-of-Life Care, and Place of Care and Death in Hong Kong. A Population-Based Telephone Survey of 1067 Adults.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017 Apr 1;18(4):367.e19-367.e27. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2016.12.066. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28214237
-
Variations in the quality and costs of end-of-life care, preferences and palliative outcomes for cancer patients by place of death: the QUALYCARE study.BMC Cancer. 2010 Aug 2;10:400. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-400. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20678203 Free PMC article.
-
Choiceless options: when hospital-based services represent the only palliative care offering.Pediatr Res. 2022 Mar;91(4):1001-1003. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01909-5. Epub 2021 Dec 18. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 34923578 Review.
-
A survey of hospice day services in the United Kingdom & Republic of Ireland : how did hospices offer social support to palliative care patients, pre-pandemic?BMC Palliat Care. 2022 Oct 5;21(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12904-022-01061-9. BMC Palliat Care. 2022. PMID: 36195870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in trends in discharge location in a cohort of hospitalized patients with cancer and non-cancer diagnoses receiving specialist palliative care: A retrospective cohort study.Palliat Med. 2023 Sep;37(8):1241-1251. doi: 10.1177/02692163231183009. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Palliat Med. 2023. PMID: 37452565 Free PMC article.
-
Association between opioid use disorder and palliative care: a cohort study using linked health administrative data in Ontario, Canada.CMAJ. 2024 Apr 28;196(16):E547-E557. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.231419. CMAJ. 2024. PMID: 38684285 Free PMC article.
-
Developing Compassionate Community: Insights from the International Standards for Community Development.Health Open Res. 2024 Sep 12;6:17. doi: 10.12688/healthopenres.13611.2. eCollection 2024. Health Open Res. 2024. PMID: 40852047 Free PMC article.
-
The instrumental value of advance directives: lesson learned from the COVID-19 pandemic for policymaking.Res Health Serv Reg. 2025 Feb 5;4(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s43999-025-00060-6. Res Health Serv Reg. 2025. PMID: 39907962 Free PMC article.
-
How initial policy responses to COVID-19 contributed to shaping dying at home preferences and care provision: key informant perspectives from Canada.BMC Health Serv Res. 2023 Nov 30;23(1):1330. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10340-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023. PMID: 38037107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pivodic L, Pardon K, Morin L, Addington-Hall J, Miccinesi G, Cardenas-Turanzas M, et al. Place of death in the population dying from diseases indicative of palliative care need: a cross-national population-level study in 14 countries. J Epidemiol Community Heal. 2016;70(1):17–24. doi: 10.1136/jech-2014-205365. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Pevenage I, Durivage P, Dequin A-M, Hamel-Roy L. Do older adults wish to die at home (and can they?). In: Billette V, Marier P, Seguin A-M, editors. Getting Wise about Getting Old: Debunking Myths about Aging. Vancouver: Purich Books; 2020. p. 207–214.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous