Cardiomyocyte-specific knockout of ADAM17 ameliorates left ventricular remodeling and function in diabetic cardiomyopathy of mice
- PMID: 35909160
- PMCID: PMC9339545
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01054-3
Cardiomyocyte-specific knockout of ADAM17 ameliorates left ventricular remodeling and function in diabetic cardiomyopathy of mice
Abstract
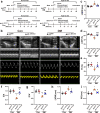
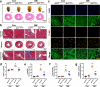
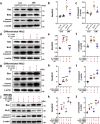
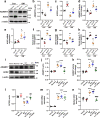
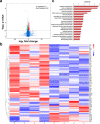
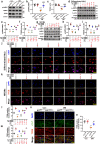
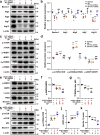
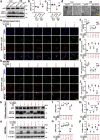
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) has proven beneficial in attenuating diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) but has been found to be a substrate of a disintegrin and metalloprotease protein-17 (ADAM17). However, whether ADAM17 plays a role in the pathogenesis and intervention of DCM is obscure. In this study, we created cardiomyocyte-specific knockout of ADAM17 (A17α-MHCKO) mice, and left ventricular dimension, function, pathology and molecular biology were assessed in ADAM17fl/fl control, A17α-MHCKO control, ADAM17fl/fl diabetic and A17α-MHCKO diabetic mice. Both differentiated H9c2 cells and neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs) were used to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of ADAM17 on DCM. The results showed that protein expression and activity of ADAM17 were upregulated whereas the protein expression of ACE2 was downregulated in the myocardium of diabetic mice. Cardiomyocyte-specific knockout of ADAM17 mitigated cardiac fibrosis and cardiomyocyte apoptosis and ameliorated cardiac dysfunction in mice with DCM. Bioinformatic analyses detected a number of genes enriched in metabolic pathways, in particular the AMPK signaling pathway, expressed differentially between the hearts of A17α-MHCKO and ADAM17fl/fl diabetic mice. The mechanism may involve activated AMPK pathway, increased autophagosome formation and improved autophagic flux, which reduced the apoptotic response in cardiomyocytes. In addition, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) might act as an upstream mediator of upregulated ADAM17 and ADAM17 might affect AMPK signaling via α1 A-adrenergic receptor (ADRA1A). These results indicated that ADAM17 activity and ACE2 shedding were enhanced in DCM, which was reversed by cardiomyocyte-specific ADAM17 knockout. Thus, inhibition of ADAM17 may provide a promising approach to the treatment of DCM.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiomyocyte-specific knockout of ADAM17 alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via inhibiting TNFα-TRAF3-TAK1-MAPK axis.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 16;9(1):273. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01977-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39406701 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo1 deletion mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy by maintaining mitochondrial dynamics via ERK/Drp1 pathway.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 20;24(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02625-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40114130 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy by activating the AMPK-paraoxonase 1 signaling axis in mice.Clin Sci (Lond). 2017 Jul 7;131(15):1877-1893. doi: 10.1042/CS20170271. Print 2017 Aug 1. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28559425
-
Novel insights into the central protective role of ACE2 in diabetic cardiomyopathy: from underlying signaling pathways to therapeutic perspectives.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3535-3551. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05196-6. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39928210 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of cardiac pathology in diabetes - Experimental insights.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 May;1864(5 Pt B):1949-1959. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.10.035. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29109032 Review.
Cited by
-
Canagliflozin mitigates ferroptosis and improves myocardial oxidative stress in mice with diabetic cardiomyopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 14;13:1011669. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1011669. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36313744 Free PMC article.
-
circHIPK3 prevents cardiac senescence by acting as a scaffold to recruit ubiquitin ligase to degrade HuR.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 31;12(17):7550-7566. doi: 10.7150/thno.77630. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36438474 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes mellitus status modifies the association between N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide and all-cause mortality risk in ischemic heart failure: a prospective cohort study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 Apr 11;15(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01046-5. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 37041629 Free PMC article.
-
The association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Oct;31(5):2237-2244. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01273-2. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37418101 Review.
-
The role of toll-like receptors (TLRs) and their therapeutic applications in glomerulonephritis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Nov;55(11):2845-2856. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03592-3. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37060433 Review.
References
-
- Heidenreich PA, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022;79:1757–1780. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.12.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

