Inhibition of Non-specific Amplification in Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification via Tetramethylammonium Chloride
- PMID: 35909465
- PMCID: PMC9326409
- DOI: 10.1007/s13206-022-00070-3
Inhibition of Non-specific Amplification in Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification via Tetramethylammonium Chloride
Abstract
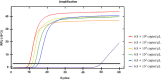
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) may be used in molecular and point-of-care diagnostics for pathogen detection. The amplification occurs under isothermal conditions using up to six primers. However, non-specific amplification is frequently observed in LAMP. Non-specific amplification has the potential to be triggered by forward and reverse internal primers. And the relatively low reaction temperature (55-65 °C) induces the secondary structure via primer-primer interactions. Primer redesign and probe design have been recommended to solve this problem. LAMP primers have strict conditions, such as Tm, GC contents, primer dimer, and distance between primers compared to conventional PCR primers. Probe design requires specialized knowledge to have high specificity for a target. In polymerase chain reaction (PCR), some chemicals or proteins are used for improving specificity and efficiency. Therefore, we hypothesized that additives can suppress the non-specific amplification. In this study, tetramethylammonium chloride (TMAC), formamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, Tween 20, and bovine serum albumin have been used as LAMP additives. In our study, TMAC was presented as a promising additive for suppressing non-specific amplification in LAMP.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13206-022-00070-3.
Keywords: Additive; Loop-mediated isothermal amplification; Non-specific amplification; Tetramethylammonium chloride.
© The Korean BioChip Society 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThere are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
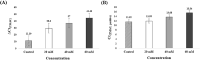
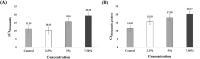
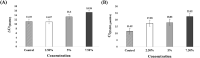
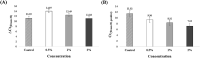
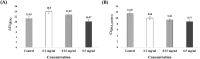
Similar articles
-
Pullulan reduces the non-specific amplification of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP).Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Feb;411(6):1211-1218. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1552-2. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30617407
-
Two methods for increased specificity and sensitivity in loop-mediated isothermal amplification.Molecules. 2015 Apr 7;20(4):6048-59. doi: 10.3390/molecules20046048. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25853320 Free PMC article.
-
Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a chromatographic lateral-flow dipstick for rapid detection of Chattonella marina.Harmful Algae. 2019 Nov;89:101666. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2019.101666. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Harmful Algae. 2019. PMID: 31672231
-
Advancements and applications of loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology: a comprehensive overview.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1406632. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1406632. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39091309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Label-Based Polymer Nanoparticles Biosensor Combined with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Rapid, Sensitive, and Highly Specific Identification of Brucella abortus.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 18;9:758564. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.758564. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34869267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Detection of Streptococcus mutans Using an Integrated Microfluidic System with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 28;33(8):1101-1110. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2304.04026. Epub 2023 May 19. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37280774 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for screening congenital cytomegalovirus infection in newborns.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;107(22):6789-6798. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12771-2. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37725139 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical and diagnostic performance characteristics of reverse-transcriptase loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for dengue virus serotypes 1-4: A scoping review to inform potential use in portable molecular diagnostic devices.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2023 Aug 8;3(8):e0002169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002169. eCollection 2023. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37552632 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Mode Graphene Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor with Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;14(2):91. doi: 10.3390/bios14020091. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392010 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Visual Detection of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium in Food Animal Meat Products.Foods. 2025 May 13;14(10):1731. doi: 10.3390/foods14101731. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40428511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuce M, Kurt H, Mokkapati VRSS, Budak H. Employment of nanomaterials in polymerase chain reaction: insight into the impacts and putative operating mechanisms of nano-additives in PCR. RSC Adv. 2014;4:36800–36814. doi: 10.1039/C4RA06144F. - DOI
-
- Mühl H, Kochem A-J, Disqué C, Sakka SG. Activity and DNA contamination of commercial polymerase chain reaction reagents for the universal 16S rDNA real-time polymerase chain reaction detection of bacterial pathogens in blood. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010;66:41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.07.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Delidow BC, Lynch JP, Peluso JJ, White BA. PCR Protocols. New Jersey: Humana Press; 1993. Polymerase Chain Reaction: Basic Protocols; pp. 1–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
