The Regulatory Effects of MicroRNAs on Tumor Immunity
- PMID: 35909469
- PMCID: PMC9329000
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2121993
The Regulatory Effects of MicroRNAs on Tumor Immunity
Abstract
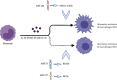
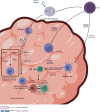
MicroRNAs are endogenous noncoding small RNAs that posttranscriptionally regulate the expressions of their target genes. Accumulating research shows that miRNAs are crucial regulators of immune cell growth and antitumor immune response. Studies on miRNAs and tumors primarily focus on the tumor itself. At the same time, relatively few studies on the indirect regulatory effects of miRNAs in the development of tumors are achieved by affecting the immune system of tumor hosts and altering their immune responses. This review discusses the influence of miRNAs on the antitumor immune system.
Copyright © 2022 Yan Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune Modulatory microRNAs Involved in Tumor Attack and Tumor Immune Escape.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017 Oct 1;109(10). doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx034. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017. PMID: 28383653 Review.
-
The Role of miRNA in Tumor Immune Escape and miRNA-Based Therapeutic Strategies.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 18;12:807895. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.807895. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35116035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs play a central role in molecular dysfunctions linking inflammation with cancer.Immunol Rev. 2013 May;253(1):167-84. doi: 10.1111/imr.12050. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23550646 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: novel regulators during the immune response.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Mar;218(3):467-72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21639. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19034913 Review.
-
Research progress on the regulation of nutrition and immunity by microRNAs in fish.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021 Jun;113:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2021.03.011. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33766547 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in Cancer Immunology: Master Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Evasion, with Therapeutic Potential.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;17(13):2172. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132172. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-Suppressive and Oncogenic Roles of microRNA-149-5p in Human Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10823. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810823. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in the abscopal effect: bridging radiotherapy and systemic anti-tumor immunity for enhanced cancer therapy.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2025 Aug 13;42(5):48. doi: 10.1007/s10585-025-10364-z. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2025. PMID: 40797149 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical