Artichoke Leaf Extract-Mediated Neuroprotection against Effects of Aflatoxin in Male Rats
- PMID: 35909495
- PMCID: PMC9325642
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4421828
Artichoke Leaf Extract-Mediated Neuroprotection against Effects of Aflatoxin in Male Rats
Abstract
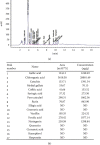
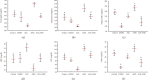
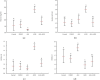
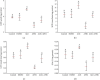
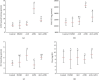
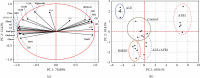
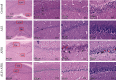
Attenuation of adverse effects of aflatoxin (AFB1) in brains of B1 rats by extracts of leaves of artichoke was studied. The active ingredients in extracts of leaves of artichoke, Cynara scolymus L., were determined by HPLC analysis. In the 42-day experiment, rats were exposed to either sterile water, 4% DMSO, 100 mg artichoke leaf extract/kg body mass, 72 μg aflatoxin B1/kg body mass, or AFB1 plus artichoke leaf extract. Neurotoxicity of AFB1 was determined by an increase in profile of lipids, augmentation of plasmatic glucose and concentrations of insulin, oxidative stress, increased activities of cholinergic enzymes, and a decrease in activities of several antioxidant enzymes and pathological changes in brain tissue. Extracts of artichoke leaf significantly reduced adverse effects caused by AFB1, rescuing most of the parameters to values similar to unexposed controls, which demonstrated that adverse, neurotoxic effects caused by aflatoxin B1 could be significantly reduced by simultaneous dietary supplementation with artichoke leaf extract, which itself is not toxic.
Copyright © 2022 Enas A. Ibrahim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effects of a chemically-characterized extract from artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) against AFB1-induced toxicity in rats.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2023 Nov;46(6):1070-1082. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2022.2129672. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36196508
-
Protective effect of artichoke (Cynara scolymus) leaf extract against lead toxicity in rat.Pharm Biol. 2013 Sep;51(9):1104-9. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.777931. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Pharm Biol. 2013. PMID: 23745593
-
Proximate Composition, Minerals and Antioxidant Activity of Artichoke Leaf Extracts.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Apr;194(2):589-595. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01806-3. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 31286388 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Studies of Artichoke Leaf Extract and Their Health Benefits.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2015 Dec;70(4):441-53. doi: 10.1007/s11130-015-0503-8. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26310198 Review.
-
The antioxidant activity of artichoke (Cynara scolymus): A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies.Phytother Res. 2019 Jan;33(1):55-71. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6213. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 30345589
Cited by
-
Artichoke (Cynara Scolymus) Methanolic Leaf Extract Alleviates Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Toxicity in BALB/c Mouse Brain: Involvement of Oxidative Stress and Apoptotically Related Klotho/PPARγ Signaling.J Pers Med. 2022 Dec 4;12(12):2012. doi: 10.3390/jpm12122012. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36556233 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of the Versatility of the Parts of the Globe Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.), Its By-Products and Dietary Supplements.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 22;16(5):599. doi: 10.3390/nu16050599. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional and Therapeutic Potential of Cynara scolymus in Health Benefits.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 17;16(6):872. doi: 10.3390/nu16060872. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Approaches to Aflatoxin B1 Control in Food and Feed Safety: Detection, Inhibition, and Mitigation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 7;26(13):6534. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136534. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
May phytophenolics alleviate aflatoxins-induced health challenges? A holistic insight on current landscape and future prospects.Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 28;9:981984. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.981984. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36386916 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Legan J. D. Cereals and cereal products. The Microbiological Safety and Quality of Food . 2000;1:759–783.
-
- Li Y., Wang J., Li J., Sun X. An improved overall risk probability-based method for assessing the combined health risks of chemical mixtures: an example about mixture of aflatoxin B1 and microcystin LR by dietary intake. Food and Chemical Toxicology . 2020;146, article 111815 doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111815. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

