Bioinformatics Analysis of the Mechanisms of Diabetic Nephropathy via Novel Biomarkers and Competing Endogenous RNA Network
- PMID: 35909518
- PMCID: PMC9329782
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.934022
Bioinformatics Analysis of the Mechanisms of Diabetic Nephropathy via Novel Biomarkers and Competing Endogenous RNA Network
Abstract
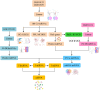
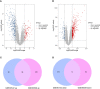
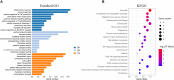
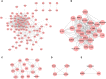
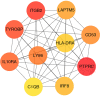
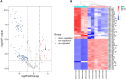
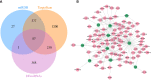
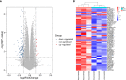
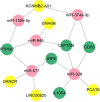
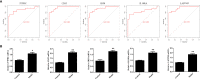
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the common chronic complications of diabetes with unclear molecular mechanisms, which is associated with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Our study intended to construct a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network via bioinformatics analysis to determine the potential molecular mechanisms of DN pathogenesis. The microarray datasets (GSE30122 and GSE30529) were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database to find differentially expressed genes (DEGs). GSE51674 and GSE155188 datasets were used to identified the differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), respectively. The DEGs between normal and DN renal tissues were performed using the Linear Models for Microarray (limma) package. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were performed to reveal the mechanisms of DEGs in the progression of DN. The protein-protein interactions (PPI) of DEGs were carried out by STRING database. The lncRNA-miRNA-messenger RNA (mRNA) ceRNA network was constructed and visualized via Cytoscape on the basis of the interaction generated through the miRDB and TargetScan databases. A total of 94 significantly upregulated and 14 downregulated mRNAs, 31 upregulated and 121 downregulated miRNAs, and nine upregulated and 81 downregulated lncRNAs were identified. GO and KEGG pathways enriched in several functions and expression pathways, such as inflammatory response, immune response, identical protein binding, nuclear factor kappa b (NF-κB) signaling pathway, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Based on the analysis of the ceRNA network, five differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) (SNHG6, KCNMB2-AS1, LINC00520, DANCR, and PCAT6), five DEmiRNAs (miR-130b-5p, miR-326, miR-374a-3p, miR-577, and miR-944), and five DEmRNAs (PTPRC, CD53, IRF8, IL10RA, and LAPTM5) were demonstrated to be related to the pathogenesis of DN. The hub genes were validated by using receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) and real-time PCR (RT-PCR). Our research identified hub genes related to the potential mechanism of DN and provided new lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network that contributed to diagnostic and potential therapeutic targets for DN.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; biomarkers; ceRNA; diabetic neuropathy; mechanisms.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Dai, Jiang and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying C1QB, ITGAM, and ITGB2 as potential diagnostic candidate genes for diabetic nephropathy using bioinformatics analysis.PeerJ. 2023 May 25;11:e15437. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15437. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37250717 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of tubulointerstitial genes and ceRNA networks involved in diabetic nephropathy via integrated bioinformatics approaches.Hereditas. 2022 Sep 26;159(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s41065-022-00249-6. Hereditas. 2022. PMID: 36154667 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analyses of biomarkers and pathways for diabetic nephropathy.Front Genet. 2023 Apr 11;14:1128136. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1128136. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37113991 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
Network pharmacology-based identification of miRNA expression of Astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Feb 4;101(5):e28747. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028747. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35119030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Depression of LncRNA DANCR alleviates tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy by regulating KLF5 through sponge miR-214-5p.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Apr 12;25(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03562-6. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38609873 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of microRNA-503 in Icariin-mediated prevention of high glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress.World J Diabetes. 2023 Aug 15;14(8):1234-1248. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i8.1234. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37664468 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic analyses reveal lysosomal-associated protein transmembrane 5 as a potential therapeutic target in lipotoxicity-induced injury in diabetic kidney disease.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2359638. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2359638. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38832484 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of transforming growth factor-β1 induce renal fibrosis based on transcriptome sequencing analysis.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Sep 28;52(5):594-604. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2022-0672. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37916309 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Identifying C1QB, ITGAM, and ITGB2 as potential diagnostic candidate genes for diabetic nephropathy using bioinformatics analysis.PeerJ. 2023 May 25;11:e15437. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15437. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37250717 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

