SIRT1 and Autophagy: Implications in Endocrine Disorders
- PMID: 35909524
- PMCID: PMC9331929
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.930919
SIRT1 and Autophagy: Implications in Endocrine Disorders
Abstract
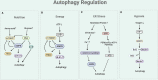
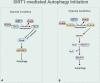
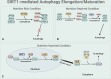
Autophagy is a cellular process involved in the selective degradation and recycling of dysfunctional intracellular components. It plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and survival by removing damaged and harmful proteins, lipids, and organelles. SIRT1, an NAD+-dependent multifunctional enzyme, is a key regulator of the autophagy process. Through its deacetylase activity, SIRT1 participates in the regulation of different steps of autophagy, from initiation to degradation. The levels and function of SIRT1 are also regulated by the autophagy process. Dysregulation in SIRT1-mediated autophagy hinders the proper functioning of the endocrine system, contributing to the onset and progression of endocrine disorders. This review provides an overview of the crosstalk between SIRT1 and autophagy and their implications in obesity, type-2 diabetes mellitus, diabetic cardiomyopathy, and hepatic steatosis.
Keywords: SIRT1; autophagy; cardiovascular disease; diabetes; diabetic cardiomyopathy; obesity.
Copyright © 2022 Kim, Mondaca-Ruff, Singh and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

