Monocyte to High-Density lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein A1 Ratios: Novel Indicators for Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 35909551
- PMCID: PMC9330493
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.935776
Monocyte to High-Density lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein A1 Ratios: Novel Indicators for Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Increasing evidence highlighted that chronic inflammation involved in the development of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This prospective study was aimed to assess the association between MetS and novel pro-inflammatory indicators like monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein and monocyte-to-apolipoprotein A1 ratios (MHR and MAR) in Chinese newly diagnosed T2DM.
Method: A total of 605 Chinese newly diagnosed T2DM with complete and available data were enrolled in this study. Demographic and anthropometric information were collected. Laboratory assessments were determined by standard methods. MetS was based on the Chinese Diabetes Society definition. Multiple binomial logistic regression model was used to estimate the independent variables of MHR and MAR for MetS. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was conducted to assess the optimal cutoff value of MHR and MAR in identifying MetS.
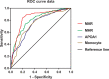
Results: Overall, the prevalence of MetS was 60.2%. The correlation analysis showed that MHR and MAR were closely correlated with metabolic risk factors like body mass index, waist circumference, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, uric acid, and insulin resistance. MHR and MAR were also significantly associated with higher odds of MetS after adjustment for other confounders, the odds ratios (ORs) (95%CI) were 1.50 (1.14-1.97) and 2.26(1.79-2.87) respectively. Furthermore, MHR and MAR were also seemed to have higher area under the curve (AUC) for MetS than ApoA1 and monocyte alone from the ROC curve analysis (P < 0.05). The AUCs of MHR and MAR identifying MetS were 0.804 (95% CI: 0.768-0.839) and 0.840 (95% CI: 0.806-0.873) respectively (P < 0.001). The optimal cutoff values of MHR and MAR were 3.57 × 108/mmol (sensitivity: 76.1%, specificity: 73.4%) and 3.95 × 108/g (sensitivity: 79.7%, specificity: 84.6%), respectively.
Conclusions: MHR and MAR were significantly associated with MetS. These two novel pro-inflammatory indicators may be useful markers for MetS in Chinese newly diagnosed T2DM.
Keywords: metabolic syndrome; monocyte to apolipoprotein A1 ratio; monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio; newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes; optimal cut-off value.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Chen, Guo and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein and apolipoprotein A1 ratios are associated with bone homeostasis imbalance caused by chronic inflammation in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 7;13:1062999. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1062999. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36419622 Free PMC article.
-
Perirenal Fat Thickness: A Surrogate Marker for Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 16;13:850334. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.850334. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35370949 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Monocyte to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio in the Presence and Severity of Metabolic Syndrome.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018 Jul;24(5):828-833. doi: 10.1177/1076029617741362. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018. PMID: 29212375 Free PMC article.
-
Interrelationships among metabolic syndrome, bone-derived cytokines, and the most common metabolic syndrome-related diseases negatively affecting bone quality.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Sep 6;16(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01440-7. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39238022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of the apolipoprotein B/A1 ratio and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Jun 17;23(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01235-z. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 38932877 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current Data and New Insights into the Genetic Factors of Atherogenic Dyslipidemia Associated with Metabolic Syndrome.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 12;13(14):2348. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142348. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ratio of Monocytes to HDL-Cholesterol Is Associated with Cardiovascular Risk and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;13(10):1995. doi: 10.3390/life13101995. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895377 Free PMC article.
-
Valproate-Induced Metabolic Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2023 May 22;11(5):1499. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051499. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocytes to Apolipoprotein A1 ratio is associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82994-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39733102 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Monocyte-to-High-Density Lipoprotein Ratio and Prediabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chinese Population.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Mar 2;17:1093-1103. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S451189. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38450416 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous