Effect of Levothyroxine on Older Patients With Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35909574
- PMCID: PMC9329610
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.913749
Effect of Levothyroxine on Older Patients With Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is usually treated with levothyroxine, but there is controversy as to whether SCH should be treated, especially for older patients. The aim of the systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate whether levothyroxine has a beneficial or harmful effect on older patients with SCH.
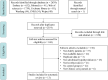
Methods: Databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Wanfang, Weipu and China National Knowledge Infrastructure were searched from inception until December 21, 2021. Subjects must be diagnosed with SCH, and older than or equal to 60 years of age. Interventions should be thyroid hormone therapy (e.g. levothyroxine). The literature was independently screened by 2 researchers. Statistical analysis was performed using RevMan5.3 software.
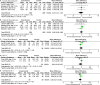
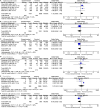
Results: A total of 13 articles were included. Meta-analysis results showed that in older SCH patients, levothyroxine can significantly reduce cholesterol (TC) (p < 0.00001), triglyceride (TG) (p < 0.00001), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (p = 0.03) and apolipoprotein B (ApoB) (p < 0.00001). In addition, levothyroxine had no significant effect on bone mineral density, fatigue, hypothyroidism symptoms, quality of life, BMI, cognitive function, depression, blood pressure, etc. in older SCH patients, and also did not significantly increase the incidence of adverse events.
Conclusions: Among older SCH patients, levothyroxine treatment may reduce TC, TG, LDL-C, and ApoB.
Keywords: apolipoprotein B; cholesterol; levothyroxine; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; older; subclinical hypothyroidism; triglyceride.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Wang, Xiao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

