Global distribution of animal sporotrichosis: A systematic review of Sporothrix sp. identified using molecular tools
- PMID: 35909607
- PMCID: PMC9325896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2022.100140
Global distribution of animal sporotrichosis: A systematic review of Sporothrix sp. identified using molecular tools
Abstract
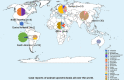
Sporotrichosis is a subcutaneous mycosis caused by thermodimorphic fungi of the genus Sporothrix. The phenotypic and genotypic differences of the isolates within the genus Sporothrix have been associated with their geographic distribution, virulence capacity, or clinical manifestation of sporotrichosis. Therefore, it is crucial to identify the causative agent of sporotrichosis. However, there are few case reports and studies in animals compared to those in humans, despite the substantial increase in the number of cases of sporotrichosis by zoonotic transmission, especially in endemic areas. Considering the epidemiological importance, taxonomic evolution and worldwide distribution of these fungi in the last decade, there is interest in identifying the species of the genus Sporothrix in different regions of the world. This study aimed to analyze the geographic distribution of animal sporotrichosis in the world, caused by pathogenic species identified by use of molecular tools. This systematic review of articles from 2007 to 2021 analyzed the geographic distribution of species that cause sporotrichosis in cats, dogs and other animals. It demonstrated that the most identified species were S. brasiliensis, isolated from cats in Brazil and S. schenckii isolated from cats in Malaysia. We show the lack of studies in global areas and reinforce the need to use molecular tools to identify and monitor potential pathogens.
Keywords: Cat diseases; Dog diseases; Sporothrix; Sporotrichosis; Systematic review.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Ansel M., Thibaut M. Une nouvelle endomycetaceae: dolichoascus nov. gen. Découverte de la reproduction sexuée par asques chez Sporotrichum schenckii (Hektoen et Perkins, 1900) C. R. Hebd. Séances l’Acadé Sci. 1970;270:2171–2173. v.
-
- Beurmann L., Gougerot H. Les Sporotrichum pathogènes. Classif. Bot. Arch. Parasitol. 1911;15:5–109. v.
-
- Boechat J.S., Oliveira M.M.E., Almeida-Paes R., Gremião I.D.F., Machado A.C.S., Oliveira R.V.C., et al. Feline sporotrichosis: associations between clinical-epidemiological profiles and phenotypic-genotypic characteristics of the etiological agents in the Rio de Janeiro epizootic area. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2018;113(3):185–196. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760170407. [S. l.], vn. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

