Evaluation of Osseointegration and Bone Healing Using Pure-Phase β - TCP Ceramic Implant in Bone Critical Defects. A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35909673
- PMCID: PMC9327785
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.859920
Evaluation of Osseointegration and Bone Healing Using Pure-Phase β - TCP Ceramic Implant in Bone Critical Defects. A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: The gold standard for osseointegration remains the autogenous bone graft, but biomaterials such as Beta - tricalcium phosphate (β - TCP) in its pure-phase showed promising results to be practical bone substitutes. This kind of implants are optimal candidates for bone integration due to their osseoconductive, biocompatibility, bioactivity, and absorptive properties.
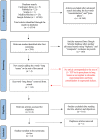
Methods: A systematic review was conducted using 5 databases (Cochrane Library, PubMed, Scielo, Medline-Bireme and Google Scholar) for searching published studies between January 1st 2011 and June 15th 2021. Only clinical and experimental studies, and case reports were included in this research. Human and animal studies published only in Portuguese or English with clinical, radiologic, and histologic evidence of new bone formation, osseoconduction, and osseointegration were included. This systematic review was reported according to PRISMA guidelines.
Results: Approximately 14.554 articles were initially found, but after advanced searching using specific including and excluding keywords, matching Boolean operators "AND," "OR" and "NOT," and after excluding duplicates, a total of 12 articles were included for this systematic review, including experimental works, a retrospective study, a randomized controlled clinical study, a randomized prospective study, a prospective observational study, and a case report. All articles showed 100% effectiveness in bone integration after β - TCP implantation by clinical, image and/or histologic assessment. Implant shape and porosity seem to have influence in osseointegration process. β - TCP can give predictable, sustainable, and adequate new bone formation with the least infection rates in implant placement cases and patient morbidity, which is the current goals for bone integration, augmentation and replacement.
Conclusion: β - TCP in its pure-phase is widely used in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery, but there is a lack of information about the use of this biomaterial for filling critical segmental defects of long bones in veterinary medicine. In this area, only experimental studies in small defects were carried out, with no clinical cases performed in animals with a longer observation time. β - TCP can produce predictable, sustainable, and adequate bone formation, with minimal infection rates and low patient morbidity. But more clinical studies in the future, demonstrating specific metric measurements in relation to bone consolidation, as well as showing results using other shapes of this implant are needed to evaluate further in depth osseoconductive and osseointegrative characteristics of this biomaterial, in order to develop new comparisons and quantitative analyses for its use in veterinary medicine as a bone replacement.
Keywords: biomaterials; bone healing; osseoconduction; osseointegration; synthetic implant; β - TCP.
Copyright © 2022 Garcia, Mingrone and Sá.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Osseointegration of Pure-Phase β-Tricalcium Phosphate (β-TCP) Ceramic Cylinder Implants in Critical Segmental Radial Bone Defects in Rabbits.Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 26;12(3):200. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12030200. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40266960 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterial selection for bone augmentation in implant dentistry: A systematic review.J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2019 Apr-Jun;10(2):46-50. doi: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_327_18. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2019. PMID: 31041181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of autogenous PRGF+β-TCP with or without a collagen membrane on bone formation and implant osseointegration in large size bone defects. A preclinical in vivo study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Aug;27(8):981-7. doi: 10.1111/clr.12742. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016. PMID: 26709196
-
Histological and Histomorphometrical Determination of the Biogradation of β-Tricalcium Phosphate Granules in Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation: A Prospective Observational Study.Implant Dent. 2017 Apr;26(2):275-283. doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000577. Implant Dent. 2017. PMID: 28301385
-
Adjuvant therapies of bone graft around non-cemented experimental orthopedic implants stereological methods and experiments in dogs.Acta Orthop Suppl. 2008 Aug;79(330):1-43. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2008. PMID: 19065776 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of a synthetic hydroxyapatite-based bone grafting material compared to established bone substitute materials on regeneration of critical-size bone defects in the ovine scapula.Regen Biomater. 2024 Apr 24;11:rbae041. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae041. eCollection 2024. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38903563 Free PMC article.
-
Modified oral implant restoration improves dental aesthetics, function, and patient satisfaction in maxillary anterior tooth loss.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Feb 15;17(2):983-991. doi: 10.62347/BDFY3122. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40092127 Free PMC article.
-
Bioglasses Versus Bioactive Calcium Phosphate Derivatives as Advanced Ceramics in Tissue Engineering: Comparative and Comprehensive Study, Current Trends, and Innovative Solutions.J Funct Biomater. 2025 May 3;16(5):161. doi: 10.3390/jfb16050161. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40422826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Tricalcium Phosphate on Healing of Non-Unions: An Observational Study of over 400 Non-Unions.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023 May 12;19:395-404. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S409119. eCollection 2023. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023. PMID: 37201037 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Osseointegration of Pure-Phase β-Tricalcium Phosphate (β-TCP) Ceramic Cylinder Implants in Critical Segmental Radial Bone Defects in Rabbits.Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 26;12(3):200. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12030200. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40266960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Javaid MA, Esfandiari SA. Health Technology Assessment Report on Role of Platelet Derived Growth Factor in Intra-Osseous Periodontal Regeneration (Report no: S2013.01). Montreal, Canada: Faculty of Dentistry, McGill University; (2013). Available online at: https://www.mcgill.ca/dentistryohs/courses-and-events/dent-655/hta-report (accessed May 28, 2022).
-
- Costa BD, Camargo NH, Oleskovicz N, Gava A, Dallabrida AL, Regalin D, et al. . Neoformação óssea e osteointegração de biomateriais micro e nanoestruturados em ovinos. Pesq Vet Bras. (2015) 35:177–87. 10.1590/S0100-736X2015000200015 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources