Inhibitory Effect of Polydatin Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infections by Reducing Aerolysin Production
- PMID: 35909695
- PMCID: PMC9330046
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.937463
Inhibitory Effect of Polydatin Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infections by Reducing Aerolysin Production
Abstract
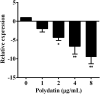
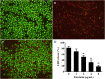
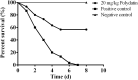
The fast-growing demand for aquatic products has led to the rapid development of aquaculture. However, diseases caused by bacterial pathogens result in severe economic losses all over the world. Although the introduction of antibiotics to aquaculture decreased the mortality of infectious diseases, the emergence of antibiotic resistance caused treatment failure. Therefore, drugs with novel strategies are needed for combatting infections caused by resistant bacterial strains. In the present study, aerolysin was identified as a target for developing drugs from natural compounds against Aeromonas hydrophila (A. hydrophila) infections. We found that polydatin without an inhibitory effect against A. hydrophila growth could decrease the hemolysis mediated by aerolysin. In both western blot and qPCR assays, the addition of polydatin decreased the production of aerolysin by downregulating the aerolysin encoding gene. Moreover, cell viability and animal studies found that polydatin could reduce the pathogenesis of A. hydrophila both in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, these findings provided a novel approach and candidate for treating resistant A. hydrophila infections in aquaculture.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; aerolysin; anti-virulence; hemolytic activity; polydatin.
Copyright © 2022 Dong, Yan, Yang, Zhou, Song, Liu, Ma, Xu, Yang and Ai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Palmatine Inhibits the Pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila by Reducing Aerolysin Expression.Foods. 2022 Oct 18;11(20):3250. doi: 10.3390/foods11203250. Foods. 2022. PMID: 37430999 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin decreases the pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila via inhibiting the activity of aerolysin.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):165-176. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1867455. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33372840 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein Inhibits the Pathogenesis of Aeromonas hydrophila by Disrupting Quorum Sensing Mediated Biofilm Formation and Aerolysin Production.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 28;12:753581. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.753581. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34650438 Free PMC article.
-
Current prospects and challenges in fish vaccine development in India with special reference to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 May;100:283-299. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.01.064. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32088285 Review.
-
A review on pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and their mitigation through medicinal herbs in aquaculture.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 28;9(3):e14088. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14088. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36938468 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

