Coapplication of Effective Microorganisms and Nanomagnesium Boosts the Agronomic, Physio-Biochemical, Osmolytes, and Antioxidants Defenses Against Salt Stress in Ipomoea batatas
- PMID: 35909720
- PMCID: PMC9326395
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.883274
Coapplication of Effective Microorganisms and Nanomagnesium Boosts the Agronomic, Physio-Biochemical, Osmolytes, and Antioxidants Defenses Against Salt Stress in Ipomoea batatas
Abstract
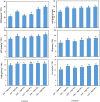
The application of bio- and nanofertilizers are undoubtedly opening new sustainable approaches toward enhancing abiotic stress tolerance in crops. In this study, we evaluated the application of effective microorganisms (EMs) of five groups belonging to photosynthetic bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, yeast, actinobacteria, and fermenting fungi combined with magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles (MgO-NP) on the growth and productivity of sweet potato plants grown in salt-affected soils. In two field experiments carried out in 2020 and 2021, we tested the impacts of EMs using two treatments (with vs. without EMs as soil drench) coupled with three foliar applications of MgO-NP (0, 50, and 100 μg ml-1 of MgO, representing MgO-NP0, MgO-NP50, and MgO-NP100, respectively). In our efforts to investigate the EMs:MgO-NP effects, the performance (growth and yield), nutrient acquisition, and physio-biochemical attributes of sweet potatoes grown in salt-affected soil (7.56 dS m-1) were assessed. Our results revealed that salinity stress significantly reduced the growth parameters, yield traits, photosynthetic pigment content (chlorophylls a and b, and carotenoids), cell membrane stability, relative water content, and nutrient acquisition of sweet potatoes. However, the EMs+ and/or MgO-NP-treated plants showed high tolerance to salt stress, specifically with a relatively superior increase when any of the biostimulants were combined. The application of EMs and/or MgO-NP improved osmotic stress tolerance by increasing the relative water content and membrane integrity. These positive responses owed to increase the osmolytes level (proline, free amino acids, and soluble sugars) and antioxidative compounds (non-enzymatic concentration, enzymatic activities, phenolic acid, and carotenoids). We also noticed that soil salinity significantly increased the Na+ content, whereas EMS+ and/or MgO-NP-treated plants exhibited lower Na+ concentration and increased K+ concentration and K+/Na+ ratio. These improvements contributed to increasing the photosynthetic pigments, growth, and yield under salinity stress. The integrative application of EMs and MgO-NP showed higher efficacy bypassing all single treatments. Our findings indicated the potential of coapplying EMs and MgO-NP for future use in attenuating salt-induced damage beneficially promoting crop performance.
Keywords: abiotic stress; antioxidant; osmoprotectants; salinity; sweet potato; tuber yield.
Copyright © 2022 Abd El-Mageed, Gyushi, Hemida, El-Saadony, Abd El-Mageed, Abdalla, AbuQamar, El-Tarabily and Abdelkhalik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abd El-Mageed T. A., El-sherif A. M. A., Abd El-Mageed S. A., Abdou N. M. (2019). A novel compost alleviate drought stress for sugar beet production grown in Cd-contaminated saline soil. Agric. Water Manag. 226:105831. 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105831 - DOI
-
- Abd El-Mageed T. A., Rady M. M., Taha R. S., El Azeam S., Simpson C. R., Semida W. M. (2020). Effects of integrated use of residual sulfur-enhanced biochar with effective microorganisms on soil properties, plant growth and short-term productivity of Capsicum annuum under salt stress. Sci. Hortic. 261:108930. 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108930 - DOI
-
- Abdelkhalik A., Pascual-Seva N., Nájera I., Domene M. Á, Baixauli C., Pascual B. (2019). Effect of deficit irrigation on the productive response of drip-irrigated onion (Allium cepa L.) in mediterranean conditions. Hortic. J. 88 488–498. 10.2503/hortj.UTD-081 - DOI
-
- Acosta-Motos J. R., Ortuño M. F., Bernal-Vicente A., Diaz-Vivancos P., Sanchez-Blanco M. J., Hernandez J. A. (2017). Plant responses to salt stress: adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 7:18. 10.3390/agronomy7010018 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

