Effect of Qiangdi 863 Nanosynergids Treated Water, Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Potassium Fertilizers on Rice Growth Physiology and Grain Quality
- PMID: 35909737
- PMCID: PMC9334000
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.916949
Effect of Qiangdi 863 Nanosynergids Treated Water, Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Potassium Fertilizers on Rice Growth Physiology and Grain Quality
Abstract
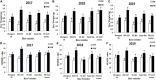
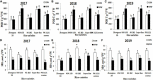
Nanotechnology is an emerging technique that helps in solving the biotic and abiotic agricultural issues leading to enhance crop productivity. Therefore, it was hypothesized to check the effect of Qiangdi 863 nano synergids biological-assisted growth apparatus and nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium (NPK) fertilizers improving rice germination, early growth, physiology, and yield. An experiment was performed on five rice varieties for three consecutive years (2017-2019). The nanosynergids-treated water (NTW) significantly improved the speed of germination (25.3, 35.6, and 32.3%), final emergence percentage (100%) and seed emergence energy percentage (80, 95, and 90%), radical (1.25, 1.7, and 2.35 cm) and plumule growth (1.29, 1.24, and 1.66 cm), soil plant analysis development (46, 45, and 47), antioxidant enzymatic activities, such as catalase activity (34,376 μg-1FW h-1, 33,264 μg-1FW h-1, and 34,453 μg-1F W h-1), superoxide dismutase (18,456 μg-1F W h-1, 19,445 μg-1F W h-1, and 19,954 μg-1F W h-1), peroxide (745 Ug-1F W, 734 Ug-1F W, and 752 Ug-1F W), production and declined malondialdehyde (4.5 μmolg-1F W, 5.1 μmolg-1F W, and 4.2 μmolg-1F W) for all years respectively in KSK 133. The application of nano-treated irrigated water enriched the biomass of rice seedlings. The overall nano synergid treatments successfully enhanced the endogenous hormones as salicylic acid (6,016.27 p mol/L, 5823.22 p mol/L, and 5922.12 p mol/L), jasmonates (JA) (5,175.6 p mol/L, 4231 p mol/L, and 5014.21 p mol/L) brassinosteroids (BR) (618.2 p mol/L, 546.83 p mol/L, and 582.1 p mol/L) quantification and yield 1000 grain weight (22.3, 22, and 23.2 g) of KSK 133. Hence, the overall results proved that NTW could effectively enhance the early growth and yield of rice varieties.
Keywords: antioxidant enzymes; brassinosteroids; jasmonates; nitrogen; phosphorous; potassium; salicylic acid; varieties.
Copyright © 2022 Younas, Yousaf, Riaz, Rashid, Aftab, Fiaz, Shamsheer and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ahmad M. S., Wu B., Wang H., Kang D. (2021). Identification of drought tolerance on the main agronomic traits for rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica) Germplasm in China. Agronomy 11:1740. 10.3390/agronomy11091740 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

