Evaluation of Roholtiella sp. Extract on Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Yield and Quality in a Hydroponic Greenhouse System
- PMID: 35909742
- PMCID: PMC9331902
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.843465
Evaluation of Roholtiella sp. Extract on Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Yield and Quality in a Hydroponic Greenhouse System
Abstract
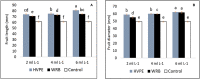
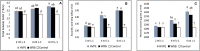
This study was carried out to investigate the impacts of cyanobacteria (Roholtiella sp.) high-value product extract (HVPE) and water resuspended biomass WRB treatments on bell pepper production using the hydroponic system under greenhouse conditions. Six cyanobacteria treatments (6 ml L-1, 4 ml L-1, and 2 ml L-1 - HVPE, 6 ml L-1, 4 ml L-1, and 2 ml L-1 - WRB, and TR0 as control) were evaluated using the foliar application method. The results showed that foliar application of HVPE with treatments of 2 ml L-1, 4 ml L-1, and 6 ml L-1 produced significantly higher values of physical growth parameters of bell pepper (BP) plants (shoot length, the number of leaves, plant leaf length, plant leaf width, and the diameter of the shoot), SPAD index, yield components (the fruit length, fruit width, the number of fruit per plant, and fresh weight per fruit), biochemical composition [ascorbic acid, phenolic acid, and total soluble solids (TSS)], and the total yield compared to the control group TR0. Also, significant higher values of growth parameters (shoot length, the number of leaves, plant leaf length, plant leaf width, the diameter of the shoot), SPAD index, yield components (the fruit length, fruit width, the number of fruits per plant, and fresh weight per fruit), biochemical composition [ascorbic acid, phenolic acid, and total soluble solids (TSS)], and the total yield were obtained with foliar spraying WRB at 2 ml L-1, 4 ml L-1, and 6 ml L-1 compared to the control group TR0. Consequently, the treated bell pepper with Roholtiella sp. HVPE and WRB were more efficient in enhancing production and chemical constituents compared with the control group.
Keywords: ascorbic acid; bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.); high-value product extract; hydroponic systems; phenolic compound; water resuspended biomass.
Copyright © 2022 Bello, Saadaoui, Ahmed, Hamdi, Cherif and Ben-Hamadou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abdelaal K. A., El-Maghraby L. M., Elansary H., Hafez Y. M., Ibrahim E. I., El-Banna M., et al. (2020). Treatment of sweet pepper with stress tolerance-inducing compounds alleviates salinity stress oxidative damage by mediating the physio-biochemical activities and antioxidant systems. Agronomy 10, 26. 10.3390/agronomy10010026 - DOI
-
- Ahmed Y., Shalaby E. (2012). Effect of different seaweed extracts and compost on vegetative growth, yield and fruit quality of cucumber. J. Hortic. Sci. Ornam. Plants 4, 233–240. 10.5829/idosi.jhsop.2012.4.3.252 - DOI
-
- AOAC International . (2016). Official Methods of Analysis, 20th Edn. Rockville, MD: AOAC International.
-
- Barone V., Baglieri A., Stevanato P., Broccanello C., Bertoldo G., Bertaggia M., et al. (2018). Root morphological and molecular responses induced by microalgae extracts in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). J. Appl. Phycol. 30, 1061–1071. 10.1007/s10811-017-1283-3 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

