Looking for peptides from rice starch processing by-product: Bioreactor production, anti-tyrosinase and anti-inflammatory activity, and in silico putative taste assessment
- PMID: 35909767
- PMCID: PMC9335147
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.929918
Looking for peptides from rice starch processing by-product: Bioreactor production, anti-tyrosinase and anti-inflammatory activity, and in silico putative taste assessment
Abstract
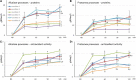
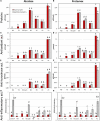
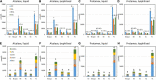
One of the major challenges for the modern society, is the development of a sustainable economy also aiming at the valorization of agro-industrial by-products in conjunction with at a significant reduction of generated residues from farm to retail. In this context, the present study demonstrates a biotechnological approach to yield bioactive peptides from a protein fraction obtained as a by-product of the rice starch production. Enzymatic hydrolysis, with the commercial proteases Alcalase and Protamex, were optimized in bioreactor up to 2 L of volume. The two best digestates, selected with respect to peptide release and extract antioxidant capacity, were further fractionated (cut-offs of 10, 5, and 1 kDa) via cross-flow filtration. Amino acid composition indicated that most of the fractions showed positive nutritional characteristics, but a putative bitter taste. A fraction obtained with Alcalase enzyme (retentate 8 kDa) exerted anti-inflammatory potential, while the smaller molecular weight fractions (retentate 1-5 kDa and permeate < 1 kDa) were more active in tyrosinase inhibition. The latter were further sub-fractionated by size-exclusion chromatography. From the 15 most anti-tyrosinase sub-fractions, 365 peptide sequences were identified via liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry. The present data support the possible exploitation of bioactive peptide from rice starch by-product as ingredients into food, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic formulations.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory activity; anti-tyrosinase activity; antioxidants; bioactive peptides; bitter taste; rice by-product.
Copyright © 2022 Ferri, Tedeschi, Prandi, Michelini, Calabretta, Babini, Graen-Heedfeld, Bretz, Raddadi, Gianotti, Lamborghini and Tassoni.
Conflict of interest statement
ML was employed by Carminia snc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peptide Fractions Obtained from Rice By-Products by Means of an Environment-Friendly Process Show In Vitro Health-Related Bioactivities.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 26;12(1):e0170954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170954. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28125712 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic production of bioactive peptides from scotta, an exhausted by-product of ricotta cheese processing.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 30;14(12):e0226834. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226834. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31887121 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of starch industry liquid by-product to produce bioactive peptides from rice hydrolyzed proteins.Food Chem. 2014 Jul 15;155:199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.055. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24594175
-
Amended final report on the safety assessment of Oryza Sativa (rice) Bran Oil, Oryza Sativa (rice) Germ Oil, Rice Bran Acid,Oryza Sativa (rice) Bran Wax, Hydrogenated Rice Bran Wax, Oryza Sativa (rice)Bran Extract, Oryza Sativa (rice) Extract, Oryza Sativa (rice) Germ Powder, Oryza Sativa (rice) Starch, Oryza Sativa (rice) Bran, Hydrolyzed Rice Bran Extract, Hydrolyzed Rice Bran Protein, Hydrolyzed Rice Extract, and Hydrolyzed Rice Protein.Int J Toxicol. 2006;25 Suppl 2:91-120. doi: 10.1080/10915810600964626. Int J Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 17090480 Review.
-
Bioactive peptides derived from plant origin by-products: Biological activities and techno-functional utilizations in food developments - A review.Food Res Int. 2020 Oct;136:109504. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109504. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32846583 Review.
References
-
- Cohen S., Michaud D. (1993). Synthesis of a fluorescent derivatizing reagent, 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate, and its application for the analysis of hydrolysate amino acids via high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 211 279–287. 10.1006/abio.1993.1270 - DOI - PubMed
-
- FAOSTAT (2020). Food and Agriculture Data. [Online]. Available online at : http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home [Accessed December 10th 2021]
-
- Ferri M., Gianotti A., Tassoni A. (2013). Optimisation of assay conditions for the determination of antioxidant capacity and polyphenols in cereal food components. J. Food Compos. Anal. 30 94–101. 10.1016/j.jfca.2013.02.004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

