Vibration and Trajectory Tracking Control of Engineering Mechanical Arm Based on Neural Network
- PMID: 35909853
- PMCID: PMC9337976
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4461546
Vibration and Trajectory Tracking Control of Engineering Mechanical Arm Based on Neural Network
Abstract
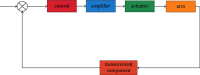
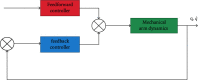
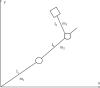
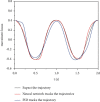
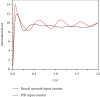
We offer a neural network-based control method to control the vibration of the engineering mechanical arm and the trajectory in order to solve the problem of large errors in tracking the path when the engineering mechanical arm is unstable and under the influence of the outside world. A mechanical arm network is used to perform tasks related to learning the unknown dynamic properties of a engineering mechanical arms keyboard without the need for prior learning. Given the dynamic equations of the engineering mechanical arm, the dynamic properties of the mechanical arm were studied using a positive feedback network. The adaptive neural network management system was developed, and the stability and integrity of the closed-loop system were proved by Lyapunov's function. Engineering mechanical arm motion trajectory control errors were modeled and validated in the Matlab/Simulink environment. The simulation results show that the management of the adaptive neural network is able to better control the desired path of the engineering mechanical arm in the presence of external interference, and the fluctuation range of input torque is small. The PID control has a large error in the expected trajectory tracking of the engineering mechanical arm, the fluctuation range of the input torque is as high as 20, and the jitter phenomenon is more serious. The use of detailed comparisons and adaptive neural network monitoring can perform well in manipulating the trajectory of the engineering mechanical arm. The engineering mechanical arm uses an adaptive neural network control method, in which the control precision of engineering mechanical arm motion trajectory can be improved and the out-of-control phenomenon of mechanical arm motion can be reduced.
Copyright © 2022 Xinjun Lei and Yunxin Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Khazaee M., Mirsalim M. A., Minaei S., Banakar A., Ghobadian B., et al. Remaining useful life (RUL) prediction of internal combustion engine timing belt based on vibration signals and artificial neural network. Neural Computing & Applications . 2021;33(13):7785–7801. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05520-3. - DOI
-
- Yang H. S., Dong C. Y., Qin X. C., Wu Y. H. Vibration and buckling analyses of fgm plates with multiple internal defects using xiga-pht and fcm under thermal and mechanical loads. Applied Mathematical Modelling . 2020;78:433–481. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.10.011. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

