Blood-Brain Barrier Alterations and Edema Formation in Different Brain Mass Lesions
- PMID: 35910247
- PMCID: PMC9334679
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.922181
Blood-Brain Barrier Alterations and Edema Formation in Different Brain Mass Lesions
Abstract
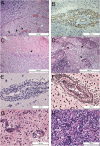
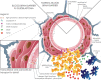
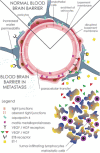
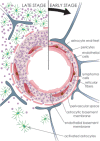
Differential diagnosis of brain lesion pathologies is complex, but it is nevertheless crucial for appropriate clinical management. Advanced imaging methods, including diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient, can help discriminate between brain mass lesions such as glioblastoma, brain metastasis, brain abscesses as well as brain lymphomas. These pathologies are characterized by blood-brain barrier alterations and have been extensively studied. However, the changes in the blood-brain barrier that are observed around brain pathologies and that contribute to the development of vasogenic brain edema are not well described. Some infiltrative brain pathologies such as glioblastoma are characterized by glioma cell infiltration in the brain tissue around the tumor mass and thus affect the nature of the vasogenic edema. Interestingly, a common feature of primary and secondary brain tumors or tumor-like brain lesions characterized by vasogenic brain edema is the formation of various molecules that lead to alterations of tight junctions and result in blood-brain barrier damage. The resulting vasogenic edema, especially blood-brain barrier disruption, can be visualized using advanced magnetic resonance imaging techniques, such as diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient. This review presents a comprehensive overview of blood-brain barrier changes contributing to the development of vasogenic brain edema around glioblastoma, brain metastases, lymphomas, and abscesses.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; brain abscess; brain edema; brain lymphoma; brain metastasis; glioblastoma multiforme.
Copyright © 2022 Solar, Hendrych, Barak, Valekova, Hermanova and Jancalek.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantitative apparent diffusion coefficients in the characterization of brain tumors and associated peritumoral edema.Acta Radiol. 2009 Jul;50(6):682-9. doi: 10.1080/02841850902933123. Acta Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19449234
-
Contribution of vasogenic and cellular edema to traumatic brain swelling measured by diffusion-weighted imaging.J Neurosurg. 1997 Dec;87(6):900-7. doi: 10.3171/jns.1997.87.6.0900. J Neurosurg. 1997. PMID: 9384402
-
Differentiation between vasogenic-edema versus tumor-infiltrative area in patients with glioblastoma during bevacizumab therapy: a longitudinal MRI study.Eur J Radiol. 2014 Jul;83(7):1250-1256. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.03.026. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Eur J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24809637 Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of Multimodal Imaging in Differentiating Vasogenic from Infiltrative Edema: A Systematic Review.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2023 Aug 21;33(4):514-521. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1772466. eCollection 2023 Oct. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37811185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Physiopathology of brain edema].Rev Neurol (Paris). 1987;143(1):3-20. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1987. PMID: 3554449 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles for efficient drug delivery and drug resistance in glioma: New perspectives.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 May;30(5):e14715. doi: 10.1111/cns.14715. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38708806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microglia after subarachnoid hemorrhage.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Jun;44(6):841-856. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241237070. Epub 2024 Feb 28. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38415607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noninvasive blood-brain barrier integrity mapping in patients with high-grade glioma and metastasis by multi-echo time-encoded arterial spin labeling.Magn Reson Med. 2025 May;93(5):2086-2098. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30415. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 39777739 Free PMC article.
-
Addition of thoracic radiotherapy to a PD-L1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy regimen delays brain metastasis onset in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer patients without baseline brain metastasis.Respir Res. 2025 Mar 5;26(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03157-1. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40045282 Free PMC article.
-
Plectin plays a role in the migration and volume regulation of astrocytes: a potential biomarker of glioblastoma.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jan 23;31(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01002-z. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38263015 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

