Fungal Mushrooms: A Natural Compound With Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 35910346
- PMCID: PMC9328747
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.925387
Fungal Mushrooms: A Natural Compound With Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
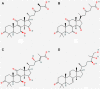
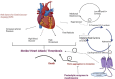
Fungi are extremely diverse in terms of morphology, ecology, metabolism, and phylogeny. Approximately, 130 medicinal activities like antitumor, immunomodulation, antioxidant, radical scavenging, cardioprotective and antiviral actions are assumed to be produced by the various varieties of medicinal mushrooms. The polysaccharides, present in mushrooms like β-glucans, micronutrients, antioxidants like glycoproteins, triterpenoids, flavonoids, and ergosterols can help establish natural resistance against infections and toxins.. Clinical trials have been performed on mushrooms like Agaricus blazei Murrill Kyowa for their anticancer effect, A. blazei Murrill for its antihypertensive and cardioprotective effects, and some other mushrooms had also been evaluated for their neurological effects. The human evaluation dose studies had been also performed and the toxicity dose was evaluated from the literature for number of mushrooms. All the mushrooms were found to be safe at a dose of 2000 mg/kg but some with mild side effects. The safety and therapeutic effectiveness of the fungal mushrooms had shifted the interest of biotechnologists toward fungal nanobiotechnology as the drug delivery system due to the vast advantages of nanotechnology systems. In complement to the vital nutritional significance of medicinal mushrooms, numerous species have been identified as sources of bioactive chemicals. Moreover, there are unanswered queries regarding its safety, efficacy, critical issues that affect the future mushroom medicine development, that could jeopardize its usage in the twenty-first century.
Keywords: Medicinal mushrooms; antiviral; cardioprotective; immune boosters; immunomodulation; radical scavenging.
Copyright © 2022 Chugh, Mittal, MP, Arora, Bhattacharya, Chopra, Cavalu and Gautam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdel-Azeem A. M., Abdel-Azeem M. A., Khalil W. F. (2019). “Endophytic Fungi as a New Source of Antirheumatoid Metabolites,” in Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Arthritis and Related Inflammatory Diseases (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier; ), 355–384. 10.1016/b978-0-12-813820-5.00021-0 - DOI
-
- Abidin M. H. Z., Abdullah N., Abidin N. Z. (2017). Therapeutic Properties ofPleurotusspecies (Oyster Mushrooms) for Atherosclerosis: A Review. Int. J. Food Prop. 20 (6), 1251–1261. 10.1080/10942912.2016.1210162 - DOI
-
- Ahn W.-S., Kim D.-J., Chae G.-T., Lee J.-M., Bae S.-M., Sin J.-I., et al. (2004). Natural Killer Cell Activity and Quality of Life Were Improved by Consumption of a Mushroom Extract, Agaricus Blazei Murill Kyowa, in Gynecological Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 14, 589–594. 10.1111/j.1048-891X.2004.14403.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources