The Role of Imaging Biomarkers to Guide Pharmacological Interventions Targeting Tumor Hypoxia
- PMID: 35910347
- PMCID: PMC9335493
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.853568
The Role of Imaging Biomarkers to Guide Pharmacological Interventions Targeting Tumor Hypoxia
Abstract
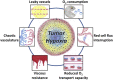
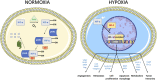
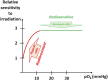
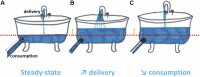
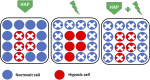
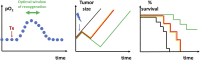
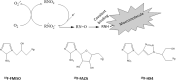
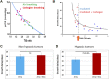
Hypoxia is a common feature of solid tumors that contributes to angiogenesis, invasiveness, metastasis, altered metabolism and genomic instability. As hypoxia is a major actor in tumor progression and resistance to radiotherapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy, multiple approaches have emerged to target tumor hypoxia. It includes among others pharmacological interventions designed to alleviate tumor hypoxia at the time of radiation therapy, prodrugs that are selectively activated in hypoxic cells or inhibitors of molecular targets involved in hypoxic cell survival (i.e., hypoxia inducible factors HIFs, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, unfolded protein response). While numerous strategies were successful in pre-clinical models, their translation in the clinical practice has been disappointing so far. This therapeutic failure often results from the absence of appropriate stratification of patients that could benefit from targeted interventions. Companion diagnostics may help at different levels of the research and development, and in matching a patient to a specific intervention targeting hypoxia. In this review, we discuss the relative merits of the existing hypoxia biomarkers, their current status and the challenges for their future validation as companion diagnostics adapted to the nature of the intervention.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; imaging; oxygen; predictive marker; theranostics; therapy; tumor hypoxia.
Copyright © 2022 Gallez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2011 Jun;11(6):393-410. doi: 10.1038/nrc3064. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21606941 Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Aug;164:152-69. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27139518 Review.
-
Imaging of Tumor Hypoxia for Radiotherapy: Current Status and Future Directions.Semin Nucl Med. 2020 Nov;50(6):562-583. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Semin Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 33059825 Review.
-
Future perspectives in melanoma research : Meeting report from the "Melanoma Bridge". Napoli, December 1st-4th 2015.J Transl Med. 2016 Nov 15;14(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-1070-y. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27846884 Free PMC article.
-
Solid tumor physiology and hypoxia-induced chemo/radio-resistance: novel strategy for cancer therapy: nitric oxide donor as a therapeutic enhancer.Nitric Oxide. 2008 Sep;19(2):205-16. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2008.04.026. Epub 2008 May 6. Nitric Oxide. 2008. PMID: 18503779 Review.
Cited by
-
The neglected burden of chronic hypoxia on the resistance of glioblastoma multiforme to first-line therapies.BMC Biol. 2024 Nov 28;22(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02075-w. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39609830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EPR Investigations to Study the Impact of Mito-Metformin on the Mitochondrial Function of Prostate Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2022 Sep 10;27(18):5872. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185872. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144606 Free PMC article.
-
From Hypoxia to Bone: Reprogramming the Prostate Cancer Metastatic Cascade.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 1;26(15):7452. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157452. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulse and CW EPR Oximetry Using Oxychip in Gemcitabine-Treated Murine Pancreatic Tumors.Mol Imaging Biol. 2024 Jun;26(3):473-483. doi: 10.1007/s11307-023-01859-w. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Mol Imaging Biol. 2024. PMID: 37784004 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the topography of spatial gene expression with interpretable deep learning.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 13:2023.10.10.561757. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.10.561757. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Methods. 2025 Feb;22(2):298-309. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02503-3. PMID: 37873258 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Adams A., van Brussel A. S., Vermeulen J. F., Mali W. P., van der Wall E., van Diest P. J., et al. (2013). The Potential of Hypoxia Markers as Target for Breast Molecular Imaging-Aa Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human Marker Expression. BMC Cancer 13, 538. 10.1186/1471-2407-13-538 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

