High-Dose Rifampicin Mediated Systemic Alterations of Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, Microbial Translocation Markers, and Acute-Phase Proteins in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- PMID: 35910352
- PMCID: PMC9335011
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.896551
High-Dose Rifampicin Mediated Systemic Alterations of Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, Microbial Translocation Markers, and Acute-Phase Proteins in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Abstract
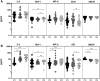
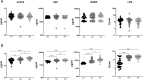
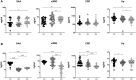
High-dose rifampicin (HDR) is now undergoing clinical trials to improve the efficacy of anti-tuberculosis treatment (ATT). However, the influence of HDR in the modulation of different cytokines, chemokines/growth factors, microbial translocation markers (MTMs), and acute-phase proteins (APPs) in pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) is not well known. PTB individuals were separated into three different arms (R10, R25, and R35) based on their rifampicin dosage. We examined the circulating levels of Type 1, Type 2, pro-inflammatory/regulatory cytokines, chemokines/growth factors, MTMs, and APPs at baseline and after completion of the second month of ATT by ELISA. The baseline levels of cytokines, chemokines/growth factors, MTMs, and APPs did not (except IL-5, IL-6, IL-17A, MCP-1, MIP-1β, GCSF, SAA, ⍺2 MG, Hp) significantly differ between the study individuals. However, at the second month, the plasma levels of Type 1 (TNFα and IFNγ), Type 2 (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13), pro-inflammatory/regulatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-17A, IL-10, and GMCSF), and APPs were significantly decreased in R35 regimen- compared to R25 and/or R10 regimen-treated PTB individuals. In contrast, the plasma levels of IL-2, IL-8, MCP-1, MIP-1β, GSF, and MTMs were significantly increased in the R35 regimen compared to R25 and/or R10 regimen-treated PTB individuals. Overall, our data reveal that HDR could potentially be beneficial for host immunity by altering different immune and inflammatory markers.
Keywords: acute-phase proteins; chemokines; cytokines; growth factors; high-dose rifampicin; microbial translocation markers; pulmonary tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2022 Kathamuthu, Bhavani, Singh, Saini, Aggarwal, Ansari, Garg and Babu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Baumann H., Gauldie J. (1990). Regulation of Hepatic Acute Phase Plasma Protein Genes by Hepatocyte Stimulating Factors and Other Mediators of Inflammation. Mol. Biol. Med. 7 (2), 147–159. - PubMed
-
- Boeree M. J., Heinrich N., Aarnoutse R., Diacon A. H., Dawson R., Rehal S., et al. (2017). High-dose Rifampicin, Moxifloxacin, and SQ109 for Treating Tuberculosis: a Multi-Arm, Multi-Stage Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 17 (1), 39–49. 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30274-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

