The potential mechanism of Longsheyangquan Decoction on the treatment of bladder cancer: Systemic network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 35910372
- PMCID: PMC9330057
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.932039
The potential mechanism of Longsheyangquan Decoction on the treatment of bladder cancer: Systemic network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
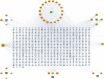
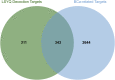
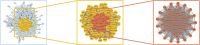
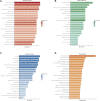
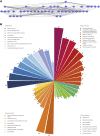
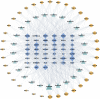
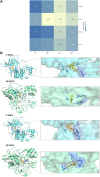
Our goal was to explore the bioactive constituents of Longsheyangquan (LSYQ) Decoction and elucidate its mechanisms on the treatment of bladder cancer (BCa). A total of 38 compounds were selected based on their pharmacokinetic properties in three large traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) databases. 654 putative targets of LSYQ Decoction were predicted using a structure-based, reverse-docking algorithm online, of which 343 overlapped with BCa-related protein-coding genes. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed to perform module analysis for further Gene Ontology (GO) annotations and Kyoto Encyclopedia Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis, which identified CDK2, EGFR, MMP9 and PTGS2 as hub targets. The TCM-compound-target network and compound-target-pathway network together revealed that quercetin, diosmetin, enhydrin and luteolin were the main components of LSYQ Decoction. Finally, molecular docking showed the affinity between the key compounds and the hub target proteins to verify the accuracy of drug target prediction in the first place. The present study deciphered the core components and targets of LSYQ Decoction on the treatment of BCa in a comprehensive systemic pharmacological manner.
Keywords: Longsheyangquan Decoction; bladder cancer; molecular docking; network pharmacology; target; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Cheng, Ye, Xu, Liang, Zhang, Chen, Dai, Ou, Mou, Li, Chen, Zhou, Zou, Mao and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Burdett S., Fisher D. J., Vale C. L., Sternberg C. N., Clarke N. W., Parmar M. K. B., et al. (2022). Adjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Eur. Urol. 81, 50–61. 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.09.028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

