Social Learning of a Spatial Task by Observation Alone
- PMID: 35910679
- PMCID: PMC9325960
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.902675
Social Learning of a Spatial Task by Observation Alone
Abstract
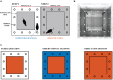
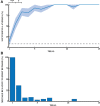
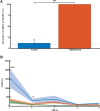
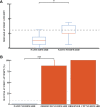
Interactions between conspecifics are central to the acquisition of useful memories in the real world. Observational learning, i.e., learning a task by observing the success or failure of others, has been reported in many species, including rodents. However, previous work in rats with NMDA-receptor blockade has shown that even extensive observation of an unexplored space through a clear barrier is not sufficient to generate a stable hippocampal representation of that space. This raises the question of whether rats can learn a spatial task in a purely observed space from watching a conspecific, and if so, does this somehow stabilize their hippocampal representation? To address these questions, we designed an observational spatial task in a two-part environment that is nearly identical to that of the aforementioned electrophysiological study, in which an observer rat watches a demonstrator animal to learn the location of a hidden reward. Our results demonstrate that rats do not need to physically explore an environment to learn a reward location, provided a conspecific demonstrates where it is. We also show that the behavioral memory is not affected by NMDA receptor blockade, suggesting that the spatial representation underlying the behavior has been consolidated by observation alone.
Keywords: learning by observation; memory; social behavior; social memory; spatial memory.
Copyright © 2022 Doublet, Nosrati and Kentros.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anzanello M. J., Fogliatto F. S. (2011). Learning curve models and applications: literature review and research directions. Int. J. Industrial Ergon. 41, 573–583. 10.1016/j.ergon.2011.05.001 - DOI
-
- Bem T., Jura B., Bontempi B., Meyrand P. (2018). Observational learning of a spatial discrimination task by rats: learning from the mistakes of others? Anim. Behav. 135, 85–96. 10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.10.018 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

