Therapeutic Potential of Different Natural Products for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 35910833
- PMCID: PMC9337964
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6873874
Therapeutic Potential of Different Natural Products for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
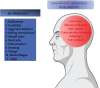
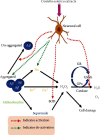
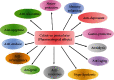
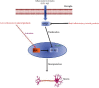
A high incidence of dementia (60-80%) and a high rate of memory loss are two of the most common symptoms of Alzheimer's disease (AD), which affects the elderly. Researchers have recommended that traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and Indian medicines can be used to prevent and cure AD. Several studies have linked neuroinflammation linked to amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition in the brain to the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disorders. As a result, more research is needed to determine the role of inflammation in neurodegeneration. Increased microglial activation, cytokine production, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) all play a role in the inflammatory process of AD. This review focuses on the role of neuroinflammation in neuroprotection and the molecular processes used by diverse natural substances, phytochemicals, and herbal formulations in distinct signaling pathways. Currently, researchers are focusing on pharmacologically active natural compounds with the anti-neuroinflammatory potential, making them a possible contender for treating AD. Furthermore, the researchers investigated the limits of past studies on TCM, Indian Ayurveda, and AD. Numerous studies have been carried out to examine the effects of medicinal whole-plant extracts on AD. Clinical investigations have shown that lignans, flavonoids, tannins, polyphenols, triterpenoids, sterols, and alkaloids have anti-inflammatory, antiamyloidogenic, anticholinesterase, and antioxidant properties. This review summarizes information about numerous medicinal plants and isolated compounds used in the treatment of AD and a list of further references.
Copyright © 2022 Biswajit Chakraborty et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-neuroinflammatory Potential of Natural Products in Attenuation of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2018 May 29;9:548. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00548. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29896105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Steroid and Terpenoid-Derived Phytochemicals to Combat Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(22):2635-2647. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666210101152352. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33463452 Review.
-
Natural product for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 26;28(5):413-423. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2016-0147. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28708573 Review.
-
Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease: The Preventive and Therapeutic Potential of Polyphenolic Nutraceuticals.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017;108:33-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28427563 Review.
-
Natural Products as Potential Anti-Alzheimer Agents.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(35):5887-5917. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190618113613. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31215372 Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal Drug Delivery by Nanotechnology: Advances in and Challenges for Alzheimer's Disease Management.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 29;16(1):58. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010058. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38258068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection by Polyherbal Medicine Divya-Medha-Vati Against Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairment Through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Acetylcholine Activity, and Cell Signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Mar;61(3):1363-1382. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03601-7. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37707741
-
Promising Natural Remedies for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy.Molecules. 2025 Feb 17;30(4):922. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040922. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Armeniacae semen amarum: a review on its botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, clinical application, toxicology and pharmacokinetics.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 23;15:1290888. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1290888. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38323080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
American Ginseng for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Jul 28;28(15):5716. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155716. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

