Roles and Functions of School Mental Health Professionals Within Comprehensive School Mental Health Systems
- PMID: 35911088
- PMCID: PMC9321305
- DOI: 10.1007/s12310-022-09535-0
Roles and Functions of School Mental Health Professionals Within Comprehensive School Mental Health Systems
Abstract
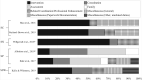
Mental health concerns are on the rise among youth, contributing to a growing need for school-based mental health services. However, challenges to service provision arise due, in part, to workforce shortages, service fragmentation, and inefficient allocation of staff time. The current study describes the professional competencies and time allocation of four school-based mental health professions (i.e., school counselors, school psychologists, school social workers, and school nurses) in order to demonstrate how schools can leverage the skills of their existing staff to coordinate a comprehensive approach to support student mental health. First, we identified the core clinical competencies needed to implement the key features of comprehensive school mental health systems. Then, we crosswalked these clinical competencies with the training standards of the four professions. Finally, we conducted a systematic review of the literature to understand how these professionals' time is allocated, as well as their responsibilities related to the provision of mental health services. Results demonstrated that, although all four professions receive training in most of the core competencies needed to implement comprehensive school mental health services, their skillsets are often underutilized in day-to-day practice. Thus, we concluded that there are at least two untapped opportunities for school leaders to support student mental health-first, maximize the use of school mental health professionals through task-shifting (i.e., reassigning tasks less central to mental health service delivery to other staff), and second, implement an integrated model of school mental health services to efficiently leverage the mental health training of professionals.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12310-022-09535-0.
Keywords: Interprofessional collaboration; Professional competencies; Roles and functions; School mental health professionals; Service coordination; Time allocation.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestWe have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Albritton K, Mathews RE, Boyle SG. Is the role of the school psychologist in early childhood truly expanding? A National survey examining school psychologists’ practices and training experiences. Journal of Applied School Psychology. 2019;35(1):1–19. doi: 10.1080/15377903.2018.1462280. - DOI
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. (2021). AAP-AACAP-CHA declaration of a national emergency in child and adolescent mental health. https://www.aap.org/en/advocacy/child-and-adolescent-healthy-mental-deve...
-
- American School Counselor Association. (n.d.-c). The role of the school counselor. https://www.schoolcounselor.org/getmedia/ee8b2e1b-d021-4575-982c-c84402c...
-
- American Nurses Association & National Association of School Nurses. (2017). School nursing: Scope and standards of practice (3rd edition). - PubMed
-
- American School Counselor Association. (2019). ASCA school counselor professional standards & competencies. https://www.schoolcounselor.org/getmedia/a8d59c2c-51de-4ec3-a565-a3235f3...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
