Application of Refined Nursing Combined with Comprehensive Treatment of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Gastrointestinal Dysfunction after Tumor Operation
- PMID: 35911141
- PMCID: PMC9328967
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4957061
Application of Refined Nursing Combined with Comprehensive Treatment of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Gastrointestinal Dysfunction after Tumor Operation
Abstract
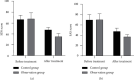
After surgical treatment, the gastrointestinal function of tumor patients is inhibited for a short time. Refined nursing is beneficial to the recovery of gastrointestinal function of tumor patients after operation. Traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine have their own advantages in the treatment of gastrointestinal dysfunction after tumor operation and the combined application of the two is more ideal. Therefore, on the premise of refined nursing, we should carefully study the efficacy of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction in tumor patients. Fifty patients with gastrointestinal dysfunction after tumor surgery admitted to Xiamen University Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital from June 2021 to August 2022 were retrospectively selected. Twenty two of them received refined care + Western medicine (control group, CG) and the other 28 received refined care + Western medicine + moxibustion and thumb-tack needle Chinese medicine (observation group, OG). We compared the recovery of gastrointestinal function, inflammatory factors, negative emotions, sleep quality, length of stay, medical expenses, and adverse reactions. The postoperative recovery effect of gastrointestinal function in the OG was better than that in the CG. The IL-8 level and TNF -α level in OG were lower than those in CG. Relative to CG, the OG had significantly low SDS scores, SAS scores, PSQ1 scores, length of hospital stay, and medical expenses. The OG incidence of adverse reactions was 28.57%; it was significantly lower than 59.09% in the CG. Refined nursing with integrated Chinese and Western medicine therapeutic interventions can promote the recovery of gastrointestinal tract function, relieve anxiety and depression, and improve sleep quality in patients with postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction after tumor surgery.
Copyright © 2022 Hongqing Su et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific nursing improves postoperative urine control function and the self-efficacy of patients undergoing radical prostatectomies.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Mar 15;14(3):1695-1704. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35422910 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of refined nursing intervention on postoperative recovery and respiratory function in lung cancer patients after thoracic surgery.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e40209. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040209. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496000 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy and psychological improvement in elderly patients with knee arthritis after comprehensive traditional Chinese medicine care.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Aug 15;14(8):5491-5500. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36105022 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of high-quality nursing intervention on negative emotions, postoperative complications and gastrointestinal function in patients with gastric cancer surgery.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Mar 15;14(3):1652-1662. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35422953 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine in treating gastrointestinal dysfunction in patients with acute stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 randomized controlled trials.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Nov;10(11):11808-11820. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2915. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34872305
Cited by
-
The role of traditional Chinese medicine in postoperative wound complications of gastric cancer.Int Wound J. 2024 Apr;21(4):e14847. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14847. Int Wound J. 2024. Retraction in: Int Wound J. 2025 Apr;22(4):e70660. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70660. PMID: 38584331 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Changes in tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a), interleukin-6 (IL-6), matrix metallopeptidase-2/9 (MMP-2/9), and T-lymphocyte subsets in patients undergoing thoracoscopic surgery under refined management for non-small-cell lung cancer.J Med Biochem. 2025 Mar 21;44(2):277-286. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-51316. J Med Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40386525 Free PMC article.
-
Demand and influencing factors of "Internet + Traditional Chinese Medicine" home nursing service for older adult patients with chronic diseases: a mixed research perspective.Front Public Health. 2023 Oct 17;11:1271082. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1271082. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37927869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Creamer F., Balfour A., Nimmo S., et al. Randomized open-label phase II study comparing oxycodone-naloxone with oxycodone in early return of gastrointestinal function after laparoscopic colorectal surgery. British Journal of Surgery . 2017;104(1):42–51. - PubMed
-
- Wang L., Ding K., Yang D., Zhao X. Management strategies of postoperative gastrointestinal tract dysfunction:a review of 210 cases. Asian Journal of Surgery . 2022;45(1):479–480. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

