Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Injection in Preventing Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity: An Analysis of Evidence from 3598 Patients
- PMID: 35911148
- PMCID: PMC9337932
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6875253
Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Injection in Preventing Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity: An Analysis of Evidence from 3598 Patients
Abstract
Background: Oxaliplatin is an effective chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of malignant tumors. However, severe oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (OIPN) has been well documented. Traditional Chinese medicine injections (TCMIs) have shown significant efficacy in preventing OIPN. However, it is difficult for clinicians to determine the differences in the efficacy of various TCMIs in preventing OIPN. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of various TCMIs in preventing OIPN through a network meta-analysis (NMA) to further inform clinical decision-making.
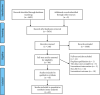
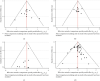
Methods: The Chinese Journal Full Text Database, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform, Chinese Science and Technology Journal Full Text Database, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, PubMed, and Embase databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of TCMIs for OIPN prevention. The retrieval time was from the establishment of the database to April 12, 2021. NMA was performed using Stata 14.0 software after 2 evaluators independently screened the literature, extracted information, and evaluated the risk of bias of the included studies.
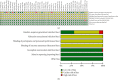
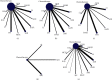
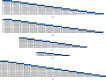
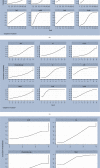
Results: A total of 45 eligible RCTs involving 3598 cancer patients and 13 TCMIs were included. The 13 TCMIs included Xiaoaiping injection (XAPI), compound kushen injection (CKSI), Aidi injection (ADI), Brucea javanica oil emulsion injection (BJOEI), Shenmai injection (SMI), Kangai injection (KAI), Astragalus injection (AI), elemene emulsion injection (EEI), Shenfu injection (SFI), Shenqi Fuzheng injection (SIFZI), Kanglaite injection (KLEI), Huachansu injection (HCSI), and lentinan injection (LI). NMA results showed that AI was superior to AD and SIFZI was superior to ADI in reducing the incidence of grade I neurotoxicity. SIFZI was superior to EEI and ADI, and BJOEI was superior to chemotherapy alone in reducing the incidence of grade II neurotoxicity. SMI was superior to LI and CKSI in reducing the incidence of grade III neurotoxicity. SIFZI was superior to LI, BJOEI, XAPI, EEI, SMI, chemotherapy alone, HCSI, KLEI, and ADI in reducing the total incidence of grade I-IV neurotoxicity. SFI was superior to ADI. Based on the SUCRA values, AI was the most likely intervention to reduce the incidence of grade I neurotoxicity, SIFZI was the most likely intervention to reduce the total incidence of grade II and I-IV neurotoxicity, and SMI was the most likely intervention to reduce the incidence of grade III and IV neurotoxicity.
Conclusion: TCMIs can prevent OIPN to some extent, among which SIFZI, SMI, and AI may be the most promising TCMIs. However, given the limitations of current studies, more well-designed, high-quality clinical trials will be needed in the future to validate the benefits of TCMIs.
Copyright © 2022 Zhi-Ying Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Network meta-analysis of 8 types of traditional Chinese medicine injection combined with chemotherapy in colorectal cancer treatment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(12):9823-9838. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04892-y. Epub 2023 May 29. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37246189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy of various CHIs combined with western medicine for non-small cell lung cancer: A bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1037620. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1037620. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36438813 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine Injections for Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 30;12:659707. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.659707. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34916929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of TCMI in Patients With Combined Coronary Heart Disease and Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 23;12:741261. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.741261. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Chinese Medicine Injection for Cardiotoxic Injury of Anthracycline Chemotherapy Drugs: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 31;2022:5800575. doi: 10.1155/2022/5800575. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9856061. doi: 10.1155/2023/9856061. PMID: 35399632 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese medicine injections with Tonifying Qi, equivalent effect of regulating energy metabolism, for acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 28;16:1511486. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1511486. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40223935 Free PMC article.
-
Summary of evidence on comprehensive healthcare for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients.Support Care Cancer. 2024 Apr 2;32(4):264. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08466-7. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38564034 Review.
-
Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Effects and Clinical Applications of Cinobufacini.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Apr;30(4):366-378. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3708-6. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38212503 Review.
References
-
- Keum N., Giovannucci E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology . 2019;16(12):713–732. - PubMed
-
- André T., Boni C., Navarro M. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology . 2009;27(19):3109–3116. - PubMed
-
- Loprinzi C. L., Qin R., Dakhil S. R., et al. Phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of intravenous calcium and magnesium to prevent oxaliplatin-induced sensory neurotoxicity (N08CB/Alliance) Journal of Clinical Oncology . 2014;32(10):997–1005. doi: 10.1200/jco.2013.52.0536. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

