Influencing Factors of Physical Activity in Patients with Lung Cancer Surgery and Its Correlation with Exercise Self-Efficacy and Perceived Social Support
- PMID: 35911150
- PMCID: PMC9325606
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7572530
Influencing Factors of Physical Activity in Patients with Lung Cancer Surgery and Its Correlation with Exercise Self-Efficacy and Perceived Social Support
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Influencing Factors of Physical Activity in Patients with Lung Cancer Surgery and Its Correlation with Exercise Self-Efficacy and Perceived Social Support.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9787301. doi: 10.1155/2023/9787301. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37501826 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of the study is to understand the current status of physical activity in patients with lung cancer surgery, explore its influencing factors, and analyze the correlation between physical activity and exercise self-efficacy and perception of social support.
Methods: The General Information Questionnaire was designed for 145 patients, Chinese version of EPIC-PAQ physical activity scale for lung cancer patients. The Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale (SEE) is used to evaluate the ability of people to organize and execute motor behaviors in various difficult situations. The Perceived Social Support Scale (PSSS) was used to emphasize individual self-understanding and self-feeling.
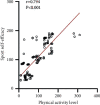
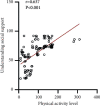
Results: The median and quartile of total physical activity scores in lung cancer surgery patients were 73.0 (34.8, 129.7) points; univariate analysis showed that there were statistically significant differences in physical activity levels among lung cancer surgery patients with different ages, work status before hospitalization, and perceived disease severity. The results of multivariate analysis showed that age, perceived disease severity, exercise self-efficacy, and total score of perceived social support affected the physical activity level of patients (P < 0.05). Efficacy were positively correlated with perceived social support (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: The level of physical activity of patients undergoing lung cancer surgery needs to be further improved. Physical activity is affected by patient age, perceived disease severity, exercise self-efficacy, and perceived social support and is positively correlated with exercise self-efficacy and perceived social support. Medical staff should provide targeted activity guidance according to the age and other characteristics of patients undergoing lung cancer surgery, enhance patients' exercise self-efficacy and comprehend social support, and improve their physical activity level, thereby promoting patients' early recovery.
Copyright © 2022 Na Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Relationship Between Facilitation of Patient Involvement and Self-Perceived Burden in Postoperative Lung Cancer Patients: The Mediating Role of Social Support.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024 Sep 24;18:1979-1989. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S464331. eCollection 2024. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024. PMID: 39345757 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived social support on objective measured sedentary behavior of stroke patients: the mediating role of exercise self-efficacy.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1444214. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1444214. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39386140 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of nutrition literacy, self-care self-efficacy and social support on the dietary practices of breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: A multicentre study.Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2023 Jun;64:102344. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2023.102344. Epub 2023 May 24. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37290159
-
The relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being among Chinese junior high school students: A chain mediating model.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1053252. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1053252. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36698574 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Telemedicine-based inspiratory muscle training and walking promotion with lung cancer survivors following curative intent therapy: a parallel-group pilot randomized trial.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Sep 1;31(9):546. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-07999-7. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37656252 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Retracted: Influencing Factors of Physical Activity in Patients with Lung Cancer Surgery and Its Correlation with Exercise Self-Efficacy and Perceived Social Support.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9787301. doi: 10.1155/2023/9787301. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37501826 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Social Support on Leisure-Time Physical Activity of the Elderly in the Chinese Village of Fuwen.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;11(15):2193. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11152193. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37570433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finnoff J. T., Awan T. M., Borg-Stein J., et al. American medical society for sports medicine position statement: principles for the responsible use of regenerative medicine in sports medicine. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine . 2021;31(6):530–541. doi: 10.1097/jsm.0000000000000973. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources