Application of General Anesthesia Combined with Saphenous Nerve-Tibial Nerve Block in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 35911159
- PMCID: PMC9325614
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7010492
Application of General Anesthesia Combined with Saphenous Nerve-Tibial Nerve Block in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Application of General Anesthesia Combined with Saphenous Nerve-Tibial Nerve Block in Total Knee Arthroplasty.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9852823. doi: 10.1155/2023/9852823. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37387818 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the saphenous nerve plus selective tibial nerve block combined with general anesthesia in total knee replacement surgery (TKRS).
Methods: Sixty-four patients who underwent unilateral TKRS between October 2019 and June 2020 were selected as study subjects. All patients were divided into the control and observation groups using the random number table method, with 32 patients in each group. Conventional general anesthesia was performed preoperatively in both groups. The control group was given an ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve block before anesthesia induction, and the observation group was given a selective tibial nerve block on the basis of the control group. The dosage of general anesthetic drugs, recovery time from general anesthesia, hemodynamic index, inflammatory response, postoperative analgesic effect, and adverse reaction rate were compared between the two groups.
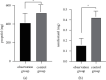
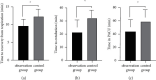
Results: Compared with the control group, the total amount of propofol and remifentanil used in the observation group was significantly less (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, patients in the observation group experienced remarkably shorter time to recovery from respiration, time to extubation, and time in the PACU (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the observation group showed a significantly reduced SBP and MAP at T2, T3, and T4, respectively, and also showed a prominently lower HR at T3 and T4 (P < 0.05). Markedly lower CRP and IL-6 levels at 6 h and 24 h after surgery were found in the observation group compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, patients receiving nerve block intervention got significantly lower VAS scores at 6 h, 24 h, and 48 h postoperatively (P < 0.05). However, there was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups of patients (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: The application of the saphenous nerve plus selective tibial nerve block combined with general anesthesia in TKRS yields a promising analgesic effect, stable hemodynamics, low levels of postoperative inflammatory responses, and high safety.
Copyright © 2022 Hong Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Observation of Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block Anesthesia on Postoperative Pain Control of Fracture Patients.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Apr 7;2022:9510669. doi: 10.1155/2022/9510669. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35432817 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided paravertebral nerve block anesthesia on the stress response and hemodynamics among lung cancer patients.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Mar 6;10(7):2174-2183. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2174. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35321160 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of nerve block combined with general anesthesia on cognitive function and postoperative pain in patients undergoing knee joint replacement.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jun 15;14(6):3915-3925. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35836865 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of general anesthesia combined with ultrasound-guided lumbosacral plexus block on hemodynamics and postoperative rehabilitation in geriatric patients with total hip arthroplasty.Afr Health Sci. 2024 Dec;24(4):299-307. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v24i4.38. Afr Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 40190546 Free PMC article.
-
Application Effect of Sevoflurane Combined with Nerve Block Anesthesia in Surgical Anesthesia in Patients with Uterine Fibroids.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jun 24;2022:9983851. doi: 10.1155/2022/9983851. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35845726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Application of General Anesthesia Combined with Saphenous Nerve-Tibial Nerve Block in Total Knee Arthroplasty.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9852823. doi: 10.1155/2023/9852823. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37387818 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of General Anesthesia in Combination with Saphenous Nerve Block-Tibial Nerve Block on Analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty and Hemodynamic Indexes.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2025 Jun;92(2):85-91. doi: 10.55095/achot2024/064. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2025. PMID: 40862588 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Flierl M. A., Sobh A. H., Culp B. M., Baker E. A., Sporer S. M. Evaluation of the painful total knee arthroplasty. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons . 2019;27(20):743–751. - PubMed
-
- Kim C. W., Kim E. K., Hong J. P. Regional anesthesia of lower extremity using tibial nerve and saphenous nerve block. Arch Plast S . 2004;31(2):239–242.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous