First Case of Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis Caused by Gemella sanguinis
- PMID: 35911324
- PMCID: PMC9335145
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26413
First Case of Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis Caused by Gemella sanguinis
Abstract
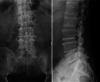
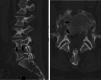
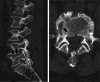
A 78-year-old man presented with back pain. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed marrow edema within the L4 and L5 vertebral bodies and a spinal epidural abscess in the spinal canal. The patient was considered to have pyogenic spondylodiscitis at the L4/L5 level. The Gram-positive cocci isolated from blood cultures were subsequently identified as Gemella sanguinis using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Symptom improvement was achieved and the infection was eradicated with conservative treatment (treatment with ceftriaxone [CTRX] and minocycline [MINO]). We report the first case of G. sanguinis-associated pyogenic spondylodiscitis. MALDI-TOF MS was useful in identifying this uncommon bacterium.
Keywords: gemella sanguinis; infection; maldi-tof ms; orthopedic disease; pyogenic spondylodiscitis.
Copyright © 2022, Hashimoto et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Vertebral osteomyelitis: long-term outcome for 253 patients from 7 Cleveland-area hospitals. McHenry MC, Easley KA, Locker GA. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:1342–1350. - PubMed
-
- Spontaneous pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis and endocarditis: incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Pigrau C, Almirante B, Flores X, et al. Am J Med. 2005;118:1287. - PubMed
-
- Osteomyelitis. Lew DP, Waldvogel FA. Lancet. 2004; 364:363–379. - PubMed
-
- Mass spectrometry tools for the classification and identification of bacteria. Sauer S, Kliem M. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8:74–82. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
