Epi-Drugs in Heart Failure
- PMID: 35911511
- PMCID: PMC9326055
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.923014
Epi-Drugs in Heart Failure
Abstract
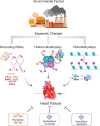
Unveiling the secrets of genome's flexibility does not only foster new research in the field, but also gives rise to the exploration and development of novel epigenetic-based therapies as an approach to alleviate disease phenotypes. A better understanding of chromatin biology (DNA/histone complexes) and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) has enabled the development of epigenetic drugs able to modulate transcriptional programs implicated in cardiovascular diseases. This particularly applies to heart failure, where epigenetic networks have shown to underpin several pathological features, such as left ventricular hypertrophy, fibrosis, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and microvascular dysfunction. Targeting epigenetic signals might represent a promising approach, especially in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), where prognosis remains poor and breakthrough therapies have yet to be approved. In this setting, epigenetics can be employed for the development of customized therapeutic approaches thus paving the way for personalized medicine. Even though the beneficial effects of epi-drugs are gaining attention, the number of epigenetic compounds used in the clinical practice remains low suggesting that more selective epi-drugs are needed. From DNA-methylation changes to non-coding RNAs, we can establish brand-new regulations for drug targets with the aim of restoring healthy epigenomes and transcriptional programs in the failing heart. In the present review, we bring the timeline of epi-drug discovery and development, thus highlighting the emerging role of epigenetic therapies in heart failure.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; epi-drugs; epigenetics; heart failure; non-coding RNAs.
Copyright © 2022 Gorica, Mohammed, Ambrosini, Calderone, Costantino and Paneni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Leveraging clinical epigenetics in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a call for individualized therapies.Eur Heart J. 2021 May 21;42(20):1940-1958. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab197. Eur Heart J. 2021. PMID: 36282124 Review.
-
Leveraging clinical epigenetics in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a call for individualized therapies.Eur Heart J. 2021 May 21;42(20):1940-1958. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab197. Eur Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33948637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic remodeling in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2022 May 1;37(3):219-226. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000961. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35275888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs in the pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 8;10:1300375. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1300375. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38259314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of epigenetic drugs in sensitizing cancers to anticancer therapies: emerging trends and clinical advancements.Epigenomics. 2023 Apr;15(8):517-537. doi: 10.2217/epi-2023-0142. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Epigenomics. 2023. PMID: 37313832 Review.
Cited by
-
The Current Therapeutic Role of Chromatin Remodeling for the Prognosis and Treatment of Heart Failure.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 16;11(2):579. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020579. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic drug screening identifies enzyme inhibitors A-196 and TMP-269 as novel regulators of sprouting angiogenesis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 10;15(1):1628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84603-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39794417 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Myocardial Fibroblasts and Its Impact on Cardiovascular Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;17(10):1353. doi: 10.3390/ph17101353. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis of RAN methylation in cardiovascular disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 30;10:1110718. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1110718. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37063953 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and Global DNA Methylation Modulation in Lipid Metabolism Disorders with a Marine-Derived Bioproduct.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;12(6):806. doi: 10.3390/biology12060806. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372091 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

