Aberrant branched-chain amino acid catabolism in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 35911554
- PMCID: PMC9334649
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.965899
Aberrant branched-chain amino acid catabolism in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
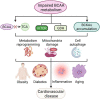
Globally, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death. Research has focused on the metabolism of carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids to improve the prognosis of cardiovascular diseases. There are three types of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs; valine, leucine, and isoleucine) required for protein homeostasis, energy balance, and signaling pathways. Increasing evidence has implicated BCAAs in the pathogenesis of multiple cardiovascular diseases. This review summarizes the biological origin, signal transduction pathways and function of BCAAs as well as their significance in cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial hypertrophy, heart failure, coronary artery disease, diabetic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia and hypertension.
Keywords: branched-chain amino acids; cardiovascular diseases; catabolism; coronary artery disease; heart failure.
Copyright © 2022 Xiong, Jiang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

