Synergistic anticancer mechanisms of curcumol and paclitaxel in triple-negative breast cancer treatment may involve down-regulating ZBTB7A expression via the NF-B signaling pathway
- PMID: 35911648
- PMCID: PMC9282748
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.64571.14218
Synergistic anticancer mechanisms of curcumol and paclitaxel in triple-negative breast cancer treatment may involve down-regulating ZBTB7A expression via the NF-B signaling pathway
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to verify whether curcumol combined with paclitaxel exerted synergistic antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects in MDA-MB-231 mammary cancer cells.
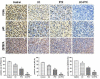
Materials and methods: The effects of different concentrations of CC, PTX, and their combination on the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 mammary cancer cells were determined by CCK-8 laboratory tests. Combination index (CI) was calculated using CompuSyn software. Colony formation assays, Hoechst 33258 immunofluorescence staining, and flow cytometry were carried out to observe proliferation and apoptosis in each group. The protein expression of PCNA, Bcl-2, Bax, ZBTB7A, p-p65, and NF-ƙB p65 was detected by western blotting. The xenograft tumor volume and body mass of nude mice were measured. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of PCNA , NF-B p65 and ZBTB7A. TUNEL and DAPI staining were used to detect the apoptosis of tumor cells.
Results: Curcumol combined with paclitaxel exerted a significant inhibitory effect on proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells in the CCK-8 laboratory test. Hoechst 33258 immunofluorescence staining, flow cytometry, TUNEL, and DAPI apoptosis staining demonstrated that cell apoptosis was the highest in the CC+PTX group in vivo and in vitro. Expression of PCNA, Bcl-2, ZBTB7A, p-p65, and NF-B p65 was lowest in the CC+PTX group, while the expression of Bax was highest. The growth of xenograft tumors in the CC+PTX group was most notably suppressed. Immunohistochemistry showed that expression of PCNA, ZBTB7A, and NF-ƙB p65 was the lowest in the CC+PTX group.
Conclusion: Curcumol combined with paclitaxel exerted a synergistic antiproliferative and proapoptotic effect on triple-negative breast cancer cells.
Keywords: Curcumol; NF-Ƙb; Paclitaxel; TNBC; ZBTB7A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes cytotoxicity of Paclitaxel through inhibiting NF-κB signaling and regulating Bax/Bcl-2 expression on triple-negative breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 May;89:227-232. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.038. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28231544
-
Apatinib enhances the anti-tumor effect of paclitaxel via the PI3K/p65/Bcl-xl pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jun;9(12):1001. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-805. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34277801 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumol triggers apoptosis of p53 mutant triple-negative human breast cancer MDA-MB 231 cells via activation of p73 and PUMA.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):1080-1088. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6273. Epub 2017 May 29. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693277 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumol enhances the anti-tumor effects of metformin via suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Aug;8(15):946. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5438. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32953746 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (p65) among Breast Cancer Patients in Cape Coast Teaching Hospital.Med Princ Pract. 2024 May 10;33(4):1-11. doi: 10.1159/000539241. Online ahead of print. Med Princ Pract. 2024. PMID: 38723618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
F-α-DDB-derivative, a novel synthetic of bifendate, plus epirubicin improves antitumor efficacy against triple negative breast cancer without additional cardiotoxicity.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 8;16(1):690. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02545-9. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40338489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Bryan BB, Schnitt SJ, Collins LC. Ductal carcinoma in situ with basal-like phenotype: a possible precursor to invasive basal-like breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 2006;19:617–621. - PubMed
-
- Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, Schneeweiss A, Barrios CH, Iwata H, et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2108–2121. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
